Thyroid follicle formation and thyroglobulin expression in multipotent endodermal stem cells
- PMID: 23360087
- PMCID: PMC3610443
- DOI: 10.1089/thy.2012.0644
Thyroid follicle formation and thyroglobulin expression in multipotent endodermal stem cells
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the impact of transcriptional induction on thyroid follicular cell (TFC) differentiation from endodermally matured embryonic stem (ES) cells. The thyroid transcription factors-NKx2 homeobox 1 (NKx2-1, formerly called TTF-1) and Paired box gene 8 (Pax8)-are known to associate biochemically and synergistically in the activation of thyroid functional genes including the sodium/iodide symporter (NIS), thyrotropin (TSH) receptor (TSHR), thyroglobulin (Tg), and thyroid peroxidase (TPO) genes. In this study, we investigated the ability of ectopically expressed Pax8 and NKx2-1 to further the induction and differentiation of murine ES cells into potential TFCs.
Methods: ES cells were stably transfected with either the Pax8 gene, the NKx2-1 gene, or both genes to study the induction of NIS, TSHR, Tg, and TPO genes as assessed using both quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and protein expression. The derived cells were cultured with or without the presence of activin A to allow their differentiation into multipotent endodermal cells.
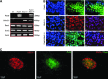
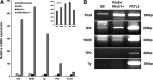
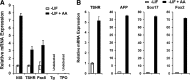
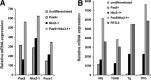
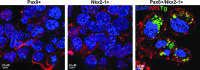
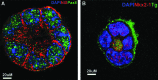
Results: The four thyroid-specific genes NIS, TSHR, Tg, and TPO were all significantly activated by expressing both transcription factors within the same ES cell. In contrast, significant but much lower transcriptional activity of the TSHR, Tg, and TPO genes was detected in cells expressing just NKx2-1, and only the NIS and TSHR genes responded to Pax8 alone. No Tg protein expression could be detected prior to their development into endodermal derivatives. However, after further differentiation of postembryoid body ES cells with activin A and TSH into endodermal cell lines, those cells with dual transfection of Pax8 and NKx2-1 demonstrated greatly enhanced expression of the NIS, TSHR, Tg, and TPO genes to such a degree that it was similar to that found in control thyroid cells. Furthermore, these same cells formed three-dimensional neofollicles in vitro and expressed Tg protein, but these phenomena were absent from lines expressing only Pax8 or NKx2-1.
Conclusion: These findings provide further evidence that co-expression of Pax8 and NKx2-1 in murine ES cells may induce the differentiation of thyroid-specific gene expression within endodermally differentiated ES cells and commit them to form three-dimensional neofollicular structures.
Figures
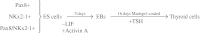
Similar articles
-
Human embryonic stem cells form functional thyroid follicles.Thyroid. 2015 Apr;25(4):455-61. doi: 10.1089/thy.2014.0537. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Thyroid. 2015. PMID: 25585054 Free PMC article.
-
TAZ Induction Directs Differentiation of Thyroid Follicular Cells from Human Embryonic Stem Cells.Thyroid. 2017 Feb;27(2):292-299. doi: 10.1089/thy.2016.0264. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Thyroid. 2017. PMID: 27829313 Free PMC article.
-
Thyrotropin-independent induction of thyroid endoderm from embryonic stem cells by activin A.Endocrinology. 2009 Apr;150(4):1970-5. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1374. Epub 2008 Dec 12. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19074581 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroglobulin regulates follicular function and heterogeneity by suppressing thyroid-specific gene expression.Biochimie. 1999 Apr;81(4):329-40. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(99)80078-9. Biochimie. 1999. PMID: 10401666 Review.
-
Iodide handling disorders (NIS, TPO, TG, IYD).Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Mar;31(2):195-212. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2017.03.006. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28648508 Review.
Cited by
-
Human embryonic stem cells form functional thyroid follicles.Thyroid. 2015 Apr;25(4):455-61. doi: 10.1089/thy.2014.0537. Epub 2015 Feb 6. Thyroid. 2015. PMID: 25585054 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of stem cells of thyroid glands in health and disease.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019 Jun;20(2):187-195. doi: 10.1007/s11154-019-09496-x. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2019. PMID: 31025266 Review.
-
The Transient Human Thyroid Progenitor Cell: Examining the Thyroid Continuum from Stem Cell to Follicular Cell.Thyroid. 2021 Aug;31(8):1151-1159. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0930. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Thyroid. 2021. PMID: 33678005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Swinging Pendulum in Treatment for Hypothyroidism: From (and Toward?) Combination Therapy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019 Jul 9;10:446. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00446. eCollection 2019. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 31354624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation and Differentiation of Adult Tissue-Derived Human Thyroid Organoids.Stem Cell Reports. 2021 Apr 13;16(4):913-925. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.02.011. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Stem Cell Reports. 2021. PMID: 33711265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Damante G. Di Lauro R. Thyroid-specific gene expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1218:255–266. - PubMed
-
- Damante G. Tell G. Di Lauro R. A unique combination of transcription factors controls differentiation of thyroid cells. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 2001;66:307–356. - PubMed
-
- Di Palma T. Nitsch R. Mascia A. Nitsch L. Di Lauro R. Zannini M. The paired domain-containing factor Pax8 and the homeodomain-containing factor TTF-1 directly interact and synergistically activate transcription. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:3395–3402. - PubMed
-
- Espinoza CR. Schmitt TL. Loos U. Thyroid transcription factor 1 and Pax8 synergistically activate the promoter of the human thyroglobulin gene. J Mol Endocrinol. 2001;27:59–67. - PubMed
-
- Lin RY. Kubo A. Keller GM. Davies TF. Committing embryonic stem cells to differentiate into thyrocyte-like cells in vitro. Endocrinology. 2003;144:2644–2649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

