Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai, China
- PMID: 23359092
- PMCID: PMC3551303
- DOI: 10.1007/s11670-011-0265-2
Prognostic Factors for Survival of Stage IB Upper Lobe Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients: A Retrospective Study in Shanghai, China
Abstract
Objective: To identify clinical and pathologic factors that were associated with the survival of stage IB upper lobe non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
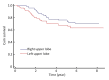
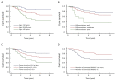
Methods: A retrospective study of 147 subjects who had undergone curative resection for stage IB upper lobe NSCLC was performed. Patients who had received any adjuvant or neo-adjuvant chemotherapy were excluded. Survival function curves were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier procedure. Crude and adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of potential prognostic factors were estimated using Cox proportional hazards models.
Results: Five factors, including age, tumor size, histologic grade of differentiation, number of removed superior mediastinal lymph node stations and presence of visceral pleura invasion, were significantly and independently associated with mortality risk. Adjusted HRs were 2.6 [95% confidence interval (95% CI): 1.1-6.5] and 4.6 (95% CI: 1.9-11) for those aged 58-68 years and those >68 years, respectively, relative to those aged <58 years. HRs for those with poorly and moderately differentiated tumors were 6.4 (95% CI: 2.3-18) and 1.4 (95% CI: 0.7-2.8), respectively. HRs for those with tumor size 3.1-5 cm and >5 cm (vs≤3.0 cm) were 2.3 (95% CI: 1.1-4.9) and 4.3 (95% CI: 1.9-10), respectively. The presence of visceral pleura invasion also increased the risk of mortality (HR=4.0, 95% CI: 1.3-12).
Conclusion: Advanced age, larger tumor size, poorly differentiated histology, smaller number of removed superior mediastinal lymph node stations, and presence of visceral pleura invasion were associated with poor survival of surgically treated stage IB upper lobe NSCLC patients.
Keywords: Lymphadenectomy; Non-small cell lung cancer; Prognosis; Stage IB.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Research for mediastinal lymph node desection style of stage Ib upper lobe non-small cell lung cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013 Nov;16(11):584-90. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2013.11.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24229624 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Prognostic significance of the non-size-based AJCC T2 descriptors: visceral pleura invasion, hilar atelectasis, or obstructive pneumonitis in stage IB non-small cell lung cancer is dependent on tumor size.Chest. 2008 Mar;133(3):662-9. doi: 10.1378/chest.07-1306. Epub 2007 Oct 9. Chest. 2008. PMID: 17925418
-
Impact of adjuvant chemotherapy on patients with stage IB non-small cell lung cancer with visceral pleural invasion.J Thorac Dis. 2024 Feb 29;16(2):875-883. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-936. Epub 2024 Feb 23. J Thorac Dis. 2024. PMID: 38505035 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of visceral pleural invasion in node-negative non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Chest. 2015 Oct;148(4):903-911. doi: 10.1378/chest.14-2765. Chest. 2015. PMID: 25675151 Review.
-
Human papillomavirus type 18: association with poor prognosis in early stage cervical cancer.J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996 Oct 2;88(19):1361-8. doi: 10.1093/jnci/88.19.1361. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1996. PMID: 8827013 Review.
Cited by
-
Time-varying pattern of postoperative recurrence risk of early-stage (T1a-T2bN0M0) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): results of a single-center study of 994 Chinese patients.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 9;9(9):e106668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0106668. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25203402 Free PMC article.
-
Cox Regression and Parametric Models: Comparison of How They Determine Factors Influencing Survival of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Dec 29;18(12):3389-3393. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3389. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 29286608 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pfannschmidt J, Muley T, Bülzebruck H, et al. Prognostic assessment after surgical resection for non-small cell lung cancer: Experiences in 2083 patients. Lung Cancer 2007;55:371-7 - PubMed
-
- Goya T, Asamura H, Yoshimura H, et al. Prognosis of 6644 resected non-small cell lung cancers in Japan: A Japanese lung cancer registry study. Lung Cancer 2005;50:227-34 - PubMed
-
- Kim AW. Lymph node drainage patterns and micrometastasis in lung cancer. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009;21:298-308 - PubMed
-
- Kotoulas CS, Foroulis CN, Kostikas K, et al. Involvement of lymphatic metastatic spread in non-small cell lung cancer accordingly to the primary cancer location. Lung Cancer 2004;44:183-91 - PubMed
-
- Rami-Porta R, Wittekind C, Goldstraw P.Complete resection in lung cancer surgery: proposed definition. Lung Cancer 2005;49:25-33 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
