The translational factor eIF3f: the ambivalent eIF3 subunit
- PMID: 23354061
- PMCID: PMC3771369
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-013-1263-y
The translational factor eIF3f: the ambivalent eIF3 subunit
Abstract
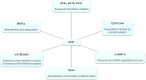
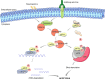
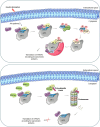
The regulation of the protein synthesis has a crucial role in governing the eukaryotic cell growth. Subtle changes of proteins involved in the translation process may alter the rate of the protein synthesis and modify the cell fate by shifting the balance from normal status into a tumoral or apoptotic one. The largest eukaryotic initiation factor involved in translation regulation is eIF3. Amongst the 13 factors constituting eIF3, the f subunit finely regulates this balance in a cell-type-specific manner. Loss of this factor causes malignancy in several cells, and atrophy in normal muscle cells. The intracellular interacting partners which influence its physiological significance in both cancer and muscle cells are detailed in this review. By delineating the global interaction network of this factor and by clarifying its intracellular role, it becomes apparent that the f subunit represents a promising candidate molecule to use for biotherapeutic applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
eIF3f: a central regulator of the antagonism atrophy/hypertrophy in skeletal muscle.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2158-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23769948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
eIF3f depletion impedes mouse embryonic development, reduces adult skeletal muscle mass and amplifies muscle loss during disuse.J Physiol. 2019 Jun;597(12):3107-3131. doi: 10.1113/JP277841. Epub 2019 May 15. J Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31026345
-
The role of eIF3 and its individual subunits in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1849(7):792-800. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.10.005. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25450521 Review.
-
The translation regulatory subunit eIF3f controls the kinase-dependent mTOR signaling required for muscle differentiation and hypertrophy in mouse.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 1;5(2):e8994. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008994. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20126553 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 3f by cyclin-dependent kinase 11 during apoptosis.FEBS Lett. 2009 Mar 18;583(6):971-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2009.02.028. Epub 2009 Feb 24. FEBS Lett. 2009. PMID: 19245811 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
eIF3f reduces tumor growth by directly interrupting clusterin with anti-apoptotic property in cancer cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5;7(14):18541-57. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8105. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26988917 Free PMC article.
-
eIF3f: a central regulator of the antagonism atrophy/hypertrophy in skeletal muscle.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;45(10):2158-62. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23769948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinicopathologic Implications of Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 3f and Her-2/neu Expression in Gastric Cancer.Clin Transl Sci. 2015 Aug;8(4):320-5. doi: 10.1111/cts.12263. Epub 2015 Feb 14. Clin Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 25684180 Free PMC article.
-
TGF beta receptor II interacting protein-1, an intracellular protein has an extracellular role as a modulator of matrix mineralization.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 24;6:37885. doi: 10.1038/srep37885. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27883077 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of the translational machinery: Variations on a common theme.Biochimie. 2015 Jul;114:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 24. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25542647 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

