Ambra1 knockdown in zebrafish leads to incomplete development due to severe defects in organogenesis
- PMID: 23348054
- PMCID: PMC3627665
- DOI: 10.4161/auto.23278
Ambra1 knockdown in zebrafish leads to incomplete development due to severe defects in organogenesis
Abstract
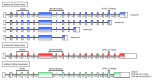
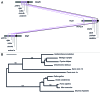
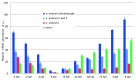
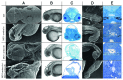
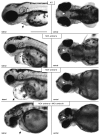
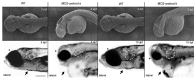
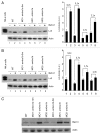
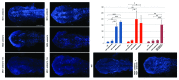
AMBRA1 is a positive regulator of the BECN1-dependent program of autophagy recently identified in mouse. In this study, we cloned the full-length cDNAs of ambra1a and ambra1b zebrafish paralogous genes. As in mouse, both Ambra1 proteins contain the characteristic WD40 repeat region. The transcripts of both genes are present as maternal RNAs in the eggs and display a gradual decline until 8 hpf, being replaced by zygotic mRNAs from 12 hpf onwards. After 24 hpf, the transcripts are mainly localized in the head, suggesting a possible role in brain development. To check their developmental roles, we adopted morpholino knockdown to block either translation (ATGMOs) or splicing (SPLICMOs). Treatment with ATGMOs causes severe embryonic malformations, as prelarvae could survive for only 3 and 4 days in ambra1a and b morphants, respectively. Treatment with SPLICMOs led to developmental defects only at a late stage, indicating the importance of maternally supplied ambra1 transcripts. Analysis of the levels of Lc3-II, an autophagosome-specific marker, in the presence of lysosome inhibitors evidenced a reduction in the rate of autophagosome formation in both MOs-injected embryos at 48 hpf, more pronounced in the case of ambra1a gene. Although some defects, such as body growth delay, curved shape and hemorrhagic pericardial cavity were present in both morphants, the occurrence of specific phenotypes, such as major abnormalities of brain development in ambra1a morphants, suggests the possible acquisition of specific functions by the two paralogous genes that are both required during development and do not compensate each other following knockdown.
Keywords: Ambra1; autophagy; development; morpholino; zebrafish.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Zebrafish ambra1a and ambra1b knockdown impairs skeletal muscle development.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 12;9(6):e99210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099210. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24922546 Free PMC article.
-
The knockdown of the maternal estrogen receptor 2a (esr2a) mRNA affects embryo transcript contents and larval development in zebrafish.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2011 May 15;172(1):120-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2010.12.020. Epub 2011 Jan 1. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21199655
-
Zebrafish ambra1a and ambra1b Silencing Affect Heart Development.Zebrafish. 2020 Apr 22. doi: 10.1089/zeb.2020.1860. Online ahead of print. Zebrafish. 2020. PMID: 32320344
-
Ambra1 at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2015 Jun 1;128(11):2003-8. doi: 10.1242/jcs.168153. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26034061 Review.
-
Ambra1 in cancer: implications for clinical oncology.Apoptosis. 2022 Oct;27(9-10):720-729. doi: 10.1007/s10495-022-01762-9. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Apoptosis. 2022. PMID: 35994214 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Functional Role of Ambra1 in Autism and Schizophrenia.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;56(10):6716-6724. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1557-7. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30915711 Review.
-
Mitophagy and Alzheimer's Disease: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms.Trends Neurosci. 2017 Mar;40(3):151-166. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Feb 9. Trends Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28190529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ambra1 spatially regulates Src activity and Src/FAK-mediated cancer cell invasion via trafficking networks.Elife. 2017 Mar 31;6:e23172. doi: 10.7554/eLife.23172. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28362576 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy in Drosophila and Zebrafish.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1208:333-356. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-2830-6_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34260032
-
Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th edition)1.Autophagy. 2021 Jan;17(1):1-382. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1797280. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33634751 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
