Design and pharmacological characterization of VUF14480, a covalent partial agonist that interacts with cysteine 98(3.36) of the human histamine H₄ receptor
- PMID: 23347159
- PMCID: PMC3764852
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.12113
Design and pharmacological characterization of VUF14480, a covalent partial agonist that interacts with cysteine 98(3.36) of the human histamine H₄ receptor
Abstract
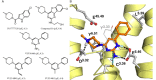
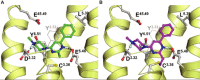
Background and purpose: The recently proposed binding mode of 2-aminopyrimidines to the human (h) histamine H₄ receptor suggests that the 2-amino group of these ligands interacts with glutamic acid residue E182(5.46) in the transmembrane (TM) helix 5 of this receptor. Interestingly, substituents at the 2-position of this pyrimidine are also in close proximity to the cysteine residue C98(3.36) in TM3. We hypothesized that an ethenyl group at this position will form a covalent bond with C98(3.36) by functioning as a Michael acceptor. A covalent pyrimidine analogue will not only prove this proposed binding mode, but will also provide a valuable tool for H4 receptor research.
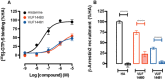
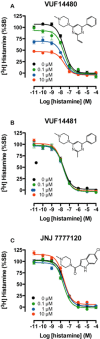
Experimental approach: We designed and synthesized VUF14480, and pharmacologically characterized this compound in hH4 receptor radioligand binding, G protein activation and β-arrestin2 recruitment experiments. The ability of VUF14480 to act as a covalent binder was assessed both chemically and pharmacologically.
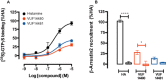
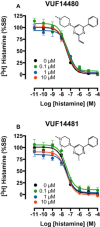
Key results: VUF14480 was shown to be a partial agonist of hH4 receptor-mediated G protein signalling and β-arrestin2 recruitment. VUF14480 bound covalently to the hH₄ receptor with submicromolar affinity. Serine substitution of C98(3.36) prevented this covalent interaction.
Conclusion and implications: VUF14480 is thought to bind covalently to the hH₄ receptor-C98(3.36) residue and partially induce hH₄ receptor-mediated G protein activation and β-arrestin2 recruitment. Moreover, these observations confirm our previously proposed binding mode of 2-aminopyrimidines. VUF14480 will be a useful tool to stabilize the receptor into an active confirmation and further investigate the structure of the active hH₄ receptor.
Keywords: GPCR; covalent binder; histamine H4 receptor; pyrimidine.
© 2013 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2013 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detailed analysis of biased histamine H₄ receptor signalling by JNJ 7777120 analogues.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(1):78-88. doi: 10.1111/bph.12117. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23351115 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of multiple histamine H₄ receptor compound classes uncovers Gαi protein- and β-arrestin2-biased ligands.Mol Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;82(6):1174-82. doi: 10.1124/mol.112.080911. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Mol Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22973061
-
Agonist-biased signaling at the histamine H4 receptor: JNJ7777120 recruits β-arrestin without activating G proteins.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;79(4):749-57. doi: 10.1124/mol.110.068395. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21134907
-
Molecular pharmacology of histamine H4 receptors.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012 Jun 1;17(6):2089-106. doi: 10.2741/4039. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2012. PMID: 22652766 Review.
-
Paradoxical stimulatory effects of the "standard" histamine H4-receptor antagonist JNJ7777120: the H4 receptor joins the club of 7 transmembrane domain receptors exhibiting functional selectivity.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Apr;79(4):631-8. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.071266. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21266488 Review.
Cited by
-
4-(3-Aminoazetidin-1-yl)pyrimidin-2-amines as High-Affinity Non-imidazole Histamine H3 Receptor Agonists with in Vivo Central Nervous System Activity.J Med Chem. 2019 Dec 12;62(23):10848-10866. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01462. Epub 2019 Nov 20. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31675226 Free PMC article.
-
Development of novel fluorescent histamine H1-receptor antagonists to study ligand-binding kinetics in living cells.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 25;8(1):1572. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19714-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29371669 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Inhibition of the Histamine H3 Receptor.Molecules. 2019 Dec 11;24(24):4541. doi: 10.3390/molecules24244541. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31835873 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Role of Serines and Threonines in Intracellular Loop 3 and C-Terminal Tail of the Histamine H4 Receptor in β-Arrestin and G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase Interaction, Internalization, and Signaling.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020 Mar 16;3(2):321-333. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00008. eCollection 2020 Apr 10. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 32296771 Free PMC article.
-
Histamine pharmacology: four years on.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;170(1):1-3. doi: 10.1111/bph.12319. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23944741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballesteros JW, Weinstein H. Integrated methods for the construction of three dimensional models and computational probing of structure funciton relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995;25:366–428.
-
- Buck E, Bourne H, Wells JA. Site-specific disulfide capture of agonist and antagonist peptides on the C5a receptor. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:4009–4012. - PubMed
-
- Chavez FCM, Edwards JP, Gomez L, Grice CA, Kearney AM, Savall BM, et al. 2008. Benzofuro- and benzothienopyrimidine modulators of the histamine H4 receptor, (Janssen Pharmaceutica NV). WO-2008008359.
-
- Chen C, Xue JC, Zhu J, Chen YW, Kunapuli S, Kim de Riel J, et al. Characterization of irreversible binding of beta-funaltrexamine to the cloned rat mu opioid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:17866–17870. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

