CALHM1 controls the Ca²⁺-dependent MEK, ERK, RSK and MSK signaling cascade in neurons
- PMID: 23345406
- PMCID: PMC4481642
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.117135
CALHM1 controls the Ca²⁺-dependent MEK, ERK, RSK and MSK signaling cascade in neurons
Abstract
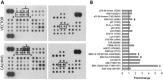
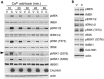
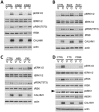
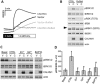
Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is a Ca(2+) channel controlling neuronal excitability and potentially involved in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Although strong evidence indicates that CALHM1 is required for neuronal electrical activity, its role in intracellular Ca(2+) signaling remains unknown. In the present study, we show that in hippocampal HT-22 cells, CALHM1 expression led to a robust and relatively selective activation of the Ca(2+)-sensing kinases ERK1/2. CALHM1 also triggered activation of MEK1/2, the upstream ERK1/2-activating kinases, and of RSK1/2/3 and MSK1, two downstream effectors of ERK1/2 signaling. CALHM1-mediated activation of ERK1/2 signaling was controlled by the small GTPase Ras. Pharmacological inhibition of CALHM1 permeability using Ruthenium Red, Zn(2+), and Gd(3+), or expression of the CALHM1 N140A and W114A mutants, which are deficient in mediating Ca(2+) influx, prevented the effect of CALHM1 on the MEK, ERK, RSK and MSK signaling cascade, demonstrating that CALHM1 controlled this pathway via its channel properties. Importantly, expression of CALHM1 bearing the natural P86L polymorphism, which leads to a partial loss of CALHM1 function and is associated with an earlier age at onset in AD patients, showed reduced activation of ERK1/2, RSK1/2/3, and MSK1. In line with these results obtained in transfected cells, primary cerebral neurons isolated from Calhm1 knockout mice showed significant impairments in the activation of MEK, ERK, RSK and MSK signaling. The present study identifies a previously uncharacterized mechanism of control of Ca(2+)-dependent ERK1/2 signaling in neurons, and further establishes CALHM1 as a critical ion channel for neuronal signaling and function.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CALHM1 and its polymorphism P86L differentially control Ca²⁺homeostasis, mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, and cell vulnerability upon exposure to amyloid β.Aging Cell. 2015 Dec;14(6):1094-102. doi: 10.1111/acel.12403. Epub 2015 Sep 29. Aging Cell. 2015. PMID: 26416646 Free PMC article.
-
Rare variants in calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) found in early onset Alzheimer's disease patients alter calcium homeostasis.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 17;8(9):e74203. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074203. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24069280 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) regulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase docking and RSK activity.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Jul;23(14):4796-804. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.14.4796-4804.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12832467 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium homeostasis modulator (CALHM) ion channels.Pflugers Arch. 2016 Mar;468(3):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s00424-015-1757-6. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Pflugers Arch. 2016. PMID: 26603282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The RSK factors of activating the Ras/MAPK signaling cascade.Front Biosci. 2008 May 1;13:4258-75. doi: 10.2741/3003. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 18508509 Review.
Cited by
-
The Polysite Pharmacology of TREK K2P Channels.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1349:51-65. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4254-8_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 35138610 Free PMC article.
-
CALHM1 deficiency impairs cerebral neuron activity and memory flexibility in mice.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 12;6:24250. doi: 10.1038/srep24250. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27066908 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-Handling Defects and Neurodegenerative Disease.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020 Jul 1;12(7):a035212. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035212. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020. PMID: 31427373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK1/2 activation in human taste bud cells regulates fatty acid signaling and gustatory perception of fat in mice and humans.FASEB J. 2016 Oct;30(10):3489-3500. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600422R. Epub 2016 Jun 29. FASEB J. 2016. PMID: 27358389 Free PMC article.
-
The structures and gating mechanism of human calcium homeostasis modulator 2.Nature. 2019 Dec;576(7785):163-167. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1781-3. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31776515 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

