A complete mass-spectrometric map of the yeast proteome applied to quantitative trait analysis
- PMID: 23334424
- PMCID: PMC3951219
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11835
A complete mass-spectrometric map of the yeast proteome applied to quantitative trait analysis
Abstract
Experience from different fields of life sciences suggests that accessible, complete reference maps of the components of the system under study are highly beneficial research tools. Examples of such maps include libraries of the spectroscopic properties of molecules, or databases of drug structures in analytical or forensic chemistry. Such maps, and methods to navigate them, constitute reliable assays to probe any sample for the presence and amount of molecules contained in the map. So far, attempts to generate such maps for any proteome have failed to reach complete proteome coverage. Here we use a strategy based on high-throughput peptide synthesis and mass spectrometry to generate an almost complete reference map (97% of the genome-predicted proteins) of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteome. We generated two versions of this mass-spectrometric map, one supporting discovery-driven (shotgun) and the other supporting hypothesis-driven (targeted) proteomic measurements. Together, the two versions of the map constitute a complete set of proteomic assays to support most studies performed with contemporary proteomic technologies. To show the utility of the maps, we applied them to a protein quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis, which requires precise measurement of the same set of peptides over a large number of samples. Protein measurements over 78 S. cerevisiae strains revealed a complex relationship between independent genetic loci, influencing the levels of related proteins. Our results suggest that selective pressure favours the acquisition of sets of polymorphisms that adapt protein levels but also maintain the stoichiometry of functionally related pathway members.
Figures
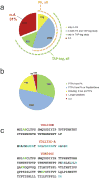

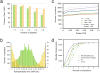
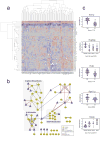
Comment in
-
Mass spectrometry mapmaking.Nat Methods. 2013 Mar;10(3):192. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2392. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23570042 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Reproducibility of combinatorial peptide ligand libraries for proteome capture evaluated by selected reaction monitoring.J Proteomics. 2013 Aug 26;89:215-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.05.037. Epub 2013 Jun 7. J Proteomics. 2013. PMID: 23747450
-
Yeast proteome map (last update).Proteomics. 2009 Oct;9(20):4669-73. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200900273. Proteomics. 2009. PMID: 19743426
-
Libraries of specific assays covering whole proteomes: from yeast to man.Clin Chem. 2010 Oct;56(10):1521-2. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2010.147900. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Clin Chem. 2010. PMID: 20693309 No abstract available.
-
Mass-Spectrometry-Based Near-Complete Draft of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Proteome.J Proteome Res. 2021 Feb 5;20(2):1328-1340. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00721. Epub 2021 Jan 14. J Proteome Res. 2021. PMID: 33443437 Review.
-
The proteome of baker's yeast mitochondria.Mitochondrion. 2017 Mar;33:15-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2016.08.007. Epub 2016 Aug 14. Mitochondrion. 2017. PMID: 27535110 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex-centric proteome profiling by SEC-SWATH-MS for the parallel detection of hundreds of protein complexes.Nat Protoc. 2020 Aug;15(8):2341-2386. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-0332-6. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32690956
-
Genomics meets proteomics: identifying the culprits in disease.Hum Genet. 2014 Jun;133(6):689-700. doi: 10.1007/s00439-013-1376-2. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24135908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide barcoding for one-pot evaluation of sequence-function relationships of nanobodies.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 2;11(1):21516. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01019-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34728738 Free PMC article.
-
Demonstrating the feasibility of large-scale development of standardized assays to quantify human proteins.Nat Methods. 2014 Feb;11(2):149-55. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2763. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Nat Methods. 2014. PMID: 24317253 Free PMC article.
-
Heritability and genetic basis of protein level variation in an outbred population.Genome Res. 2014 Aug;24(8):1363-70. doi: 10.1101/gr.170506.113. Epub 2014 May 13. Genome Res. 2014. PMID: 24823668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fleischmann RD, et al. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science. 1995;269(5223):496–512. - PubMed
-
- Venter JC, et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science. 2001;291(5507):1304–51. - PubMed
-
- Uhlen M, Graslund S, Sundstrom M. A pilot project to generate affinity reagents to human proteins. Nat Methods. 2008;5(10):854–5. - PubMed
-
- Taussig MJ, et al. ProteomeBinders: planning a European resource of affinity reagents for analysis of the human proteome. Nat Methods. 2007;4(1):13–7. - PubMed
-
- Berglund L, et al. A genecentric Human Protein Atlas for expression profiles based on antibodies. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008;7(10):2019–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

