Mechanism and implications of CXCR4-mediated integrin activation by Porphyromonas gingivalis
- PMID: 23331495
- PMCID: PMC4123224
- DOI: 10.1111/omi.12021
Mechanism and implications of CXCR4-mediated integrin activation by Porphyromonas gingivalis
Abstract
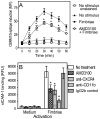
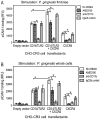
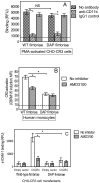
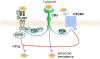
In monocytes and macrophages, the interaction of Porphyromonas gingivalis with Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) leads to the activation of a MyD88-dependent antimicrobial pathway and a phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K) -dependent pro-adhesive pathway, which activates the β2 -integrin complement receptor 3 (CR3). By means of its fimbriae, P. gingivalis binds CXC-chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) and induces crosstalk with TLR2 that inhibits the MyD88-dependent antimicrobial pathway. In this paper, we investigated the impact of the P. gingivalis-CXCR4 interaction on the pro-adhesive pathway. Using human monocytes, mouse macrophages, or receptor-transfected cell lines, we showed that the binding of P. gingivalis fimbriae to CXCR4 induces CR3 activation via PI3K, albeit in a TLR2-independent manner. An isogenic strain of P. gingivalis expressing mutant fimbriae that do not interact with CXCR4 failed to efficiently activate CR3, leading to enhanced susceptibility to killing in vivo compared with the wild-type organism. This in vivo observation is consistent with previous findings that activated CR3 mediates safe entry of P. gingivalis into macrophages. Taken together with our previous work, these results indicate that the interaction of P. gingivalis with CXCR4 leads to inhibition of antimicrobial responses and enhancement of pro-adhesive responses, thereby maximizing its adaptive fitness in the mammalian host.
Keywords: CXCR4; Porphyromonas gingivalis; Toll-like receptor 2; immune evasion; integrin; periodontitis.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

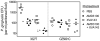
Similar articles
-
Complement receptor 3 blockade promotes IL-12-mediated clearance of Porphyromonas gingivalis and negates its virulence in vivo.J Immunol. 2007 Aug 15;179(4):2359-67. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.4.2359. J Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17675497
-
Pathogen induction of CXCR4/TLR2 cross-talk impairs host defense function.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Sep 9;105(36):13532-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0803852105. Epub 2008 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18765807 Free PMC article.
-
TLR2 transmodulates monocyte adhesion and transmigration via Rac1- and PI3K-mediated inside-out signaling in response to Porphyromonas gingivalis fimbriae.J Immunol. 2006 Jun 15;176(12):7645-56. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.12.7645. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16751412
-
Subversion of innate immunity by periodontopathic bacteria via exploitation of complement receptor-3.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;632:203-19. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-78952-1_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 19025124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis interactions with complement receptor 3 (CR3): innate immunity or immune evasion?Front Biosci. 2007 May 1;12:4547-57. doi: 10.2741/2409. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17485396 Review.
Cited by
-
Porphyromonas gingivalis virulence factors involved in subversion of leukocytes and microbial dysbiosis.Virulence. 2015;6(3):236-43. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2014.999567. Virulence. 2015. PMID: 25654623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Venous Thromboembolism and Periodontal Diseases: A Bioinformatics Analysis.Dis Markers. 2021 Dec 10;2021:1776567. doi: 10.1155/2021/1776567. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34925639 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperlipidemia impaired innate immune response to periodontal pathogen porphyromonas gingivalis in apolipoprotein E knockout mice.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 16;8(8):e71849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071849. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23977160 Free PMC article.
-
The potential crosstalk genes and molecular mechanisms between glioblastoma and periodontitis.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 12;14(1):5970. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56577-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38472293 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and Chronic Pain from Facial Skin and Oral Mucosa: Unique Neurobiology and Challenging Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 28;22(11):5810. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115810. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071720 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burns E, Bachrach G, Shapira L, Nussbaum G. Cutting Edge: TLR2 is required for the innate response to Porphyromonas gingivalis: Activation leads to bacterial persistence and TLR2 deficiency attenuates induced alveolar bone resorption. J Immunol. 2006;177:8296–8300. - PubMed
-
- Campbell JJ, Hedrick J, Zlotnik A, Siani MA, Thompson DA, Butcher EC. Chemokines and the arrest of lymphocytes rolling under flow conditions. Science. 1998;279:381–384. - PubMed
-
- Caron E, Hall A. Identification of two distinct mechanisms of phagocytosis controlled by different Rho GTPases. Science. 1998;282:1717–1721. - PubMed
-
- Constantin G, Majeed M, Giagulli C, et al. Chemokines trigger immediate b2 integrin affinity and mobility changes: differential regulation and roles in lymphocyte arrest under flow. Immunity. 2000;13:759–769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

