Purification and characterisation of immunoglobulins from the Australian black flying fox (Pteropus alecto) using anti-fab affinity chromatography reveals the low abundance of IgA
- PMID: 23308125
- PMCID: PMC3538733
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052930
Purification and characterisation of immunoglobulins from the Australian black flying fox (Pteropus alecto) using anti-fab affinity chromatography reveals the low abundance of IgA
Abstract
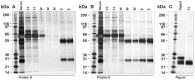
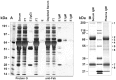
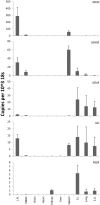
There is now an overwhelming body of evidence that implicates bats in the dissemination of a long list of emerging and re-emerging viral agents, often causing illnesses or death in both animals and humans. Despite this, there is a paucity of information regarding the immunological mechanisms by which bats coexist with highly pathogenic viruses. Immunoglobulins are major components of the adaptive immune system. Early studies found bats may have quantitatively lower antibody responses to model antigens compared to conventional laboratory animals. To further understand the antibody response of bats, the present study purified and characterised the major immunoglobulin classes from healthy black flying foxes, Pteropus alecto. We employed a novel strategy, where IgG was initially purified and used to generate anti-Fab specific antibodies. Immobilised anti-Fab specific antibodies were then used to capture other immunoglobulins from IgG depleted serum. While high quantities of IgM were successfully isolated from serum, IgA was not. Only trace quantities of IgA were detected in the serum by mass spectrometry. Immobilised ligands specific to IgA (Jacalin, Peptide M and staphylococcal superantigen-like protein) also failed to capture P. alecto IgA from serum. IgM was the second most abundant serum antibody after IgG. A survey of mucosal secretions found IgG was the dominant antibody class rather than IgA. Our study demonstrates healthy P. alecto bats have markedly less serum IgA than expected. Higher quantities of IgG in mucosal secretions may be compensation for this low abundance or lack of IgA. Knowledge and reagents developed within this study can be used in the future to examine class-specific antibody response within this important viral host.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
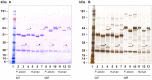
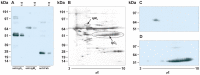
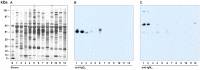
Similar articles
-
Studies on B Cells in the Fruit-Eating Black Flying Fox (Pteropus alecto).Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 14;10:489. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00489. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30930908 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of specific antibody responses to vaccination in variable flying foxes (Pteropus hypomelanus).Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009 Sep;32(5):379-94. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2007.11.002. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 18242703 Free PMC article.
-
Role of immunoglobulin classes in experimental histoplasmosis in bats.Dev Comp Immunol. 1982 Summer;6(3):557-67. doi: 10.1016/s0145-305x(82)80042-6. Dev Comp Immunol. 1982. PMID: 6982182
-
Immunoglobulin purification by affinity chromatography using protein A mimetic ligands prepared by combinatorial chemical synthesis.Immunol Invest. 2002 Aug-Nov;31(3-4):263-78. doi: 10.1081/imm-120016245. Immunol Invest. 2002. PMID: 12472184 Review.
-
Fundamental Characteristics of Bat Interferon Systems.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Dec 11;10:527921. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.527921. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33363045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Duration of Maternal Antibodies against Canine Distemper Virus and Hendra Virus in Pteropid Bats.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e67584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067584. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826322 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Insights Into Immune Systems of Bats.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 24;11:26. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00026. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Landscape of IGH germline genes of Chiroptera and the pattern of Rhinolophus affinis bat IGH CDR3 repertoire.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Apr 2;12(4):e0376223. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03762-23. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38465979 Free PMC article.
-
Studies on B Cells in the Fruit-Eating Black Flying Fox (Pteropus alecto).Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 14;10:489. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00489. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30930908 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus, the King Who Wanted More Than a Crown: From Common to the Highly Pathogenic SARS-CoV-2, Is the Key in the Accessory Genes?Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 14;12:682603. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.682603. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34335504 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hall L, Richards G (2000) Flying-foxes: fruit- and blossom-bats of Australia. Sydney: UNSW Press.
-
- Halpin K, Young PL, Field HE, Mackenzie JS (2000) Isolation of Hendra virus from pteropid bats: a natural reservoir of Hendra virus. J Gen Virol 81: 1927–1932. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

