Space exploration by the promoter of a long human gene during one transcription cycle
- PMID: 23303786
- PMCID: PMC3575846
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks1441
Space exploration by the promoter of a long human gene during one transcription cycle
Abstract
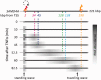
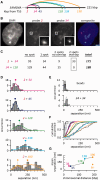
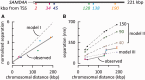
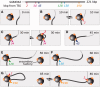
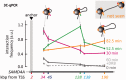
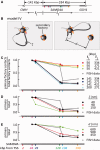
An RNA polymerase has been thought to transcribe by seeking out a promoter, initiating and then tracking down the template. We add tumor necrosis factor α to primary human cells, switch on transcription of a 221-kb gene and monitor promoter position during the ensuing transcription cycle (using RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization coupled to super-resolution localization, chromosome conformation capture and Monte Carlo simulations). Results are consistent with a polymerase immobilized in a 'factory' capturing a promoter and reeling in the template, as the transcript and promoter are extruded. Initially, the extruded promoter is tethered close to the factory and so likely to re-initiate; later, the tether becomes long enough to allow re-initiation in another factory. We suggest close tethering underlies enhancer function and transcriptional 'bursting'.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic reconfiguration of long human genes during one transcription cycle.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jul;32(14):2738-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00179-12. Epub 2012 May 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22586273 Free PMC article.
-
Active RNA polymerases: mobile or immobile molecular machines?PLoS Biol. 2010 Jul 13;8(7):e1000419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000419. PLoS Biol. 2010. PMID: 20644712 Free PMC article.
-
The topology of transcription by immobilized polymerases.Exp Cell Res. 1996 Dec 15;229(2):167-73. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0355. Exp Cell Res. 1996. PMID: 8986593 Review.
-
The effect of the DNA conformation on the rate of NtrC activated transcription of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase.sigma(54) holoenzyme.J Mol Biol. 2000 Jul 21;300(4):709-25. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.3921. J Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10891265
-
Transcription regulation by repressosome and by RNA polymerase contact.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998;63:1-9. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1998.63.1. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1998. PMID: 10384265 Review.
Cited by
-
Super-resolution measurement of distance between transcription sites using RNA FISH with intronic probes.Methods. 2016 Apr 1;98:150-157. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.11.009. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Methods. 2016. PMID: 26564237 Free PMC article.
-
Splicing of many human genes involves sites embedded within introns.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 19;43(9):4721-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv386. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25897131 Free PMC article.
-
Super-resolution molecular and functional imaging of nanoscale architectures in life and materials science.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014 Jun 12;2:20. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2014.00020. eCollection 2014. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25152893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Large distances separate coregulated genes in living Drosophila embryos.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jul 23;116(30):15062-15067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1908962116. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31285341 Free PMC article.
-
The 3D Genome as Moderator of Chromosomal Communication.Cell. 2016 Mar 10;164(6):1110-1121. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.007. Cell. 2016. PMID: 26967279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P. Molecular Biology of the Cell. New York: Garland Science; 2002.
-
- Cook PR. A model for all genomes: the role of transcription factories. J. Mol. Biol. 2010;395:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Eskiw CH, Rapp A, Carter DR, Cook PR. RNA polymerase II activity is located on the surface of protein-rich transcription factories. J. Cell Sci. 2008;121:1999–2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

