Gleevec, an Abl family inhibitor, produces a profound change in cell shape and migration
- PMID: 23300967
- PMCID: PMC3534684
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052233
Gleevec, an Abl family inhibitor, produces a profound change in cell shape and migration
Abstract
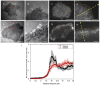
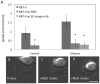
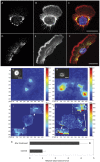
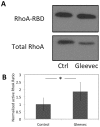
The issue of how contractility and adhesion are related to cell shape and migration pattern remains largely unresolved. In this paper we report that Gleevec (Imatinib), an Abl family kinase inhibitor, produces a profound change in the shape and migration of rat bladder tumor cells (NBTII) plated on collagen-coated substrates. Cells treated with Gleevec adopt a highly spread D-shape and migrate more rapidly with greater persistence. Accompanying this more spread state is an increase in integrin-mediated adhesion coupled with increases in the size and number of discrete adhesions. In addition, both total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM) and interference reflection microscopy (IRM) revealed a band of small punctate adhesions with rapid turnover near the cell leading margin. These changes led to an increase in global cell-substrate adhesion strength, as assessed by laminar flow experiments. Gleevec-treated cells have greater RhoA activity which, via myosin activation, led to an increase in the magnitude of total traction force applied to the substrate. These chemical and physical alterations upon Gleevec treatment produce the dramatic change in morphology and migration that is observed.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
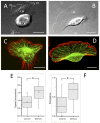
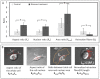
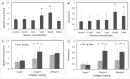
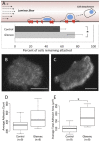
Similar articles
-
Computational analysis of the binding specificity of Gleevec to Abl, c-Kit, Lck, and c-Src tyrosine kinases.J Am Chem Soc. 2013 Oct 2;135(39):14741-53. doi: 10.1021/ja405939x. Epub 2013 Sep 20. J Am Chem Soc. 2013. PMID: 24001034 Free PMC article.
-
Gleevec target Abl important for normal immune activation of T cells.Cancer Biol Ther. 2004 Aug;3(8):704. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15751157 No abstract available.
-
Variola and monkeypox viruses utilize conserved mechanisms of virion motility and release that depend on abl and SRC family tyrosine kinases.J Virol. 2011 Jan;85(1):21-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01814-10. Epub 2010 Oct 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 20962097 Free PMC article.
-
Rho-signaling pathways in chronic myelogenous leukemia.Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Dec;8(4):261-7. doi: 10.2174/187152908786786241. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 19075636 Review.
-
Gleevec resistance: lessons for target-directed drug development.Cell Cycle. 2003 May-Jun;2(3):190-1. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 12734421 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Depletion of Arg/Abl2 improves endothelial cell adhesion and prevents vascular leak during inflammation.Angiogenesis. 2021 Aug;24(3):677-693. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09781-x. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Angiogenesis. 2021. PMID: 33770321 Free PMC article.
-
Vinculin phosphorylation differentially regulates mechanotransduction at cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesions.J Cell Biol. 2014 Apr 28;205(2):251-63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201309092. Epub 2014 Apr 21. J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24751539 Free PMC article.
-
Rotation of stress fibers as a single wheel in migrating fish keratocytes.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 17;8(1):10615. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28875-z. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30018412 Free PMC article.
-
The Focal Adhesion Analysis Server: a web tool for analyzing focal adhesion dynamics.F1000Res. 2013 Mar 4;2:68. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.2-68.v1. eCollection 2013. F1000Res. 2013. PMID: 24358855 Free PMC article.
-
Nanograting structure promotes lamellipodia-based cell collective migration and wound healing.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014;2014:2916-9. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2014.6944233. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2014. PMID: 25570601 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, et al. (2003) Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302: 1704–1709. - PubMed
-
- Webb DJ, Zhang H, Horwitz AF (2005) Cell migration: an overview. Methods Mol Biol 294: 3–11. - PubMed
-
- Franz CM, Jones GE, Ridley AJ (2002) Cell migration in development and disease. Dev Cell 2: 153–158. - PubMed
-
- Schwartzberg PL, Stall AM, Hardin JD, Bowdish KS, Humaran T, et al. (1991) Mice homozygous for the ablm1 mutation show poor viability and depletion of selected B and T cell populations. Cell 65: 1165–1175. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Boast S, de los Santos K, Schieren I, Quiroz M, et al. (2000) Mice deficient in Abl are osteoporotic and have defects in osteoblast maturation. Nat Genet 24: 304–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

