Interaction of the transactivation domain of B-Myb with the TAZ2 domain of the coactivator p300: molecular features and properties of the complex
- PMID: 23300815
- PMCID: PMC3534135
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052906
Interaction of the transactivation domain of B-Myb with the TAZ2 domain of the coactivator p300: molecular features and properties of the complex
Abstract
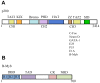
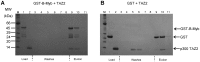
The transcription factor B-Myb is a key regulator of the cell cycle in vertebrates, with activation of transcription involving the recognition of specific DNA target sites and the recruitment of functional partner proteins, including the coactivators p300 and CBP. Here we report the results of detailed studies of the interaction between the transactivation domain of B-Myb (B-Myb TAD) and the TAZ2 domain of p300. The B-Myb TAD was characterized using circular dichroism, fluorescence and NMR spectroscopy, which revealed that the isolated domain exists as a random coil polypeptide. Pull-down and spectroscopic experiments clearly showed that the B-Myb TAD binds to p300 TAZ2 to form a moderately tight (K(d) ~1.0-10 µM) complex, which results in at least partial folding of the B-Myb TAD. Significant changes in NMR spectra of p300 TAZ2 suggest that the B-Myb TAD binds to a relatively large patch on the surface of the domain (~1200 Å(2)). The apparent B-Myb TAD binding site on p300 TAZ2 shows striking similarity to the surface of CBP TAZ2 involved in binding to the transactivation domain of the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), which suggests that the structure of the B-Myb TAD-p300 TAZ2 complex may share many features with that reported for STAT1 TAD-p300 TAZ2.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
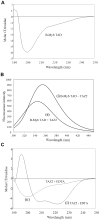
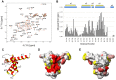
 where αN is a scaling factor of 0.2 required to account for differences in the range of amide proton and nitrogen chemical shifts. The reported positions of the helices in CBP TAZ2 (blue bars, [30]), together with those determined for p300 TAZ2 (yellow bars), are shown above the histogram. Panel C shows a ribbon representation of the backbone structure of the TAZ2 domain of CBP and panel D a contact surface view in the same orientation. In panel E the surface view of CBP TAZ2 has been rotated by 180° about the y axis. The contact surfaces have been coloured according to the magnitude of the minimal shifts induced in backbone amide resonances of equivalent residues in p300 TAZ2 by binding of the B-Myb TAD. Residues that showed a minimal shift change of less than 0.075 ppm are shown in white, over 0.15 ppm in red, and between 0.075 and 0.15 ppm are coloured according to the level of the shift on a linear gradient between white and red. No chemical shift perturbation data could be obtained for the residues shown in yellow.
where αN is a scaling factor of 0.2 required to account for differences in the range of amide proton and nitrogen chemical shifts. The reported positions of the helices in CBP TAZ2 (blue bars, [30]), together with those determined for p300 TAZ2 (yellow bars), are shown above the histogram. Panel C shows a ribbon representation of the backbone structure of the TAZ2 domain of CBP and panel D a contact surface view in the same orientation. In panel E the surface view of CBP TAZ2 has been rotated by 180° about the y axis. The contact surfaces have been coloured according to the magnitude of the minimal shifts induced in backbone amide resonances of equivalent residues in p300 TAZ2 by binding of the B-Myb TAD. Residues that showed a minimal shift change of less than 0.075 ppm are shown in white, over 0.15 ppm in red, and between 0.075 and 0.15 ppm are coloured according to the level of the shift on a linear gradient between white and red. No chemical shift perturbation data could be obtained for the residues shown in yellow.


Similar articles
-
Structural insights into TAZ2 domain-mediated CBP/p300 recruitment by transactivation domain 1 of the lymphopoietic transcription factor E2A.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4303-4315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011078. Epub 2020 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32098872 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct motifs within the p53 transactivation domain bind to the Taz2 domain of p300 and are differentially affected by phosphorylation.Biochemistry. 2009 Feb 17;48(6):1244-55. doi: 10.1021/bi801716h. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19166313 Free PMC article.
-
CBP/p300 TAZ1 domain forms a structured scaffold for ligand binding.Biochemistry. 2005 Jan 18;44(2):490-7. doi: 10.1021/bi048161t. Biochemistry. 2005. PMID: 15641773
-
Transcriptional/epigenetic regulator CBP/p300 in tumorigenesis: structural and functional versatility in target recognition.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Nov;70(21):3989-4008. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1254-4. Epub 2013 Jan 11. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23307074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The coactivators p300 and CBP have different functions during the differentiation of F9 cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 1999 Jun;77(6):481-94. doi: 10.1007/s001099900021. J Mol Med (Berl). 1999. PMID: 10475063 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and function of MuvB complexes.Oncogene. 2022 May;41(21):2909-2919. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02321-x. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35468940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into TAZ2 domain-mediated CBP/p300 recruitment by transactivation domain 1 of the lymphopoietic transcription factor E2A.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 27;295(13):4303-4315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011078. Epub 2020 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32098872 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay with the Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 complex and phosphorylation by GSK3β implicate human B-Myb in DNA-damage signaling.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 27;7:41663. doi: 10.1038/srep41663. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28128338 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into interactions of C/EBP transcriptional activators with the Taz2 domain of p300.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014 Jul;70(Pt 7):1914-21. doi: 10.1107/S1399004714009262. Epub 2014 Jun 29. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2014. PMID: 25004968 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the p300 Taz2-p53 TAD2 complex and comparison with the p300 Taz2-p53 TAD1 complex.Biochemistry. 2015 Mar 24;54(11):2001-10. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00044. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Biochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25753752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T (1996) The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 384: 641–643. - PubMed
-
- Ogryzko VV, Schiltz RL, Russanova V, Howard BH, Nakatani Y (1996) The transcriptional coactivators p300 and CBP are histone acetyltransferases. Cell 87: 953–959. - PubMed
-
- Goodman RH, Smolik S (2000) CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev 14: 1553–1577. - PubMed
-
- Janknecht R, Hunter T (1996) Transcription - A growing coactivator network. Nature 383: 22–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

