Discovery of platyhelminth-specific α/β-integrin families and evidence for their role in reproduction in Schistosoma mansoni
- PMID: 23300694
- PMCID: PMC3531407
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052519
Discovery of platyhelminth-specific α/β-integrin families and evidence for their role in reproduction in Schistosoma mansoni
Abstract
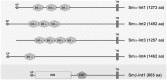
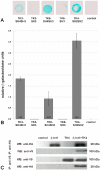
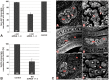
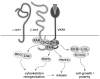
In all metazoa, the response of cells to molecular stimuli from their environment represents a fundamental principle of regulatory processes controlling cell growth and differentiation. Among the membrane-linked receptors mediating extracellular communication processes are integrin receptors. Besides managing adhesion to the extracellular matrix or to other cells, they arrange information flow into the cells by activating intracellular signaling pathways often acting synergistically through cooperation with growth factor receptors. Although a wealth of information exists on integrins in different model organisms, there is a big gap of knowledge for platyhelminths. Here we report on the in silico detection and reconstruction of α and β integrins from free-living and parasitic platyhelminths, which according to structural and phylogenetic analyses form specific clades separate from each other and from further metazoan integrins. As representative orthologs of parasitic platyhelminths we have cloned one beta-integrin (Smβ-Int1) and four alpha-integrins (Smα-Int1 - Smα-Int4) from Schistosoma mansoni; they were characterized by molecular and biochemical analyses. Evidence is provided that Smβ-Int1 interacts and co-localizes in the reproductive organs with known schistosome cellular tyrosine kinases (CTKs), of which the Syk kinase SmTK4 appeared to be the strongest interaction partner as shown by yeast two-hybrid analyses and coimmunoprecipitation experiments. By a novel RNAi approach with adult schistosomes in vitro we demonstrate for the first time multinucleated oocytes in treated females, indicating a decisive role Smβ-Int1 during oogenesis as phenotypically analyzed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). Our findings provide a first comprehensive overview about platyhelminth integrins, of which the parasite group exhibits unique features allowing a clear distinction from the free-living groups. Furthermore, we shed first lights on the functions of integrins in a trematode model parasite, revealing the complexity of molecular processes involved in its reproductive biology, which may be representative for other platyhelminths.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evidence for Integrin - Venus Kinase Receptor 1 Alliance in the Ovary of Schistosoma mansoni Females Controlling Cell Survival.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jan 23;13(1):e1006147. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006147. eCollection 2017 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28114363 Free PMC article.
-
The Syk kinase SmTK4 of Schistosoma mansoni is involved in the regulation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Feb 12;6(2):e1000769. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000769. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20169182 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptic 3' mRNA processing signals hinder the expression of Schistosoma mansoni integrins in yeast.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015 Jan-Feb;199(1-2):51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 28. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 25827755
-
Tissue-specific transcriptome analyses provide new insights into GPCR signalling in adult Schistosoma mansoni.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jan 18;14(1):e1006718. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006718. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29346437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Schistosoma mansoni: signal transduction processes during the development of the reproductive organs.Parasitology. 2010 Mar;137(3):497-520. doi: 10.1017/S0031182010000053. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Parasitology. 2010. PMID: 20163751 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analysis of male and female Schistosoma mekongi adult worms.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Sep 10;11(1):504. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3086-z. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 30201055 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins are required for tissue organization and restriction of neurogenesis in regenerating planarians.Development. 2017 Mar 1;144(5):795-807. doi: 10.1242/dev.139774. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Development. 2017. PMID: 28137894 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases and schistosome reproduction: new targets for chemotherapy.Front Genet. 2014 Jul 18;5:238. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00238. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 25101117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subtelomeric plasticity contributes to gene family expansion in the human parasitic flatworm Schistosoma mansoni.BMC Genomics. 2024 Feb 27;25(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10032-8. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38413905 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic changes modulate schistosome egg formation and are a novel target for reducing transmission of schistosomiasis.PLoS Pathog. 2014 May 8;10(5):e1004116. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004116. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24809504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fu G, Wang W, Luo BH (2012) Overview: structural biology of integrins. Methods Mol Biol 757: 81–99. - PubMed
-
- Kim C, Ye F, Ginsberg MH (2011) Regulation of integrin activation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27: 321–345. - PubMed
-
- Guo W, Giancotti FG (2004) Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5: 816–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

