Chapter 6: Structural variation and medical genomics
- PMID: 23300412
- PMCID: PMC3531322
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002821
Chapter 6: Structural variation and medical genomics
Abstract
Differences between individual human genomes, or between human and cancer genomes, range in scale from single nucleotide variants (SNVs) through intermediate and large-scale duplications, deletions, and rearrangements of genomic segments. The latter class, called structural variants (SVs), have received considerable attention in the past several years as they are a previously under appreciated source of variation in human genomes. Much of this recent attention is the result of the availability of higher-resolution technologies for measuring these variants, including both microarray-based techniques, and more recently, high-throughput DNA sequencing. We describe the genomic technologies and computational techniques currently used to measure SVs, focusing on applications in human and cancer genomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
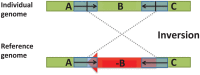
 in one genome relative to the other genome.
in one genome relative to the other genome.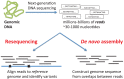

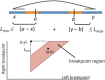
 and
and  located in orange blocks. Positions
located in orange blocks. Positions  ,
,  and the minimum
and the minimum  and maximum
and maximum  length of end-sequenced fragments constrain breakpoints
length of end-sequenced fragments constrain breakpoints  to lie within the indicated orange blocks, and are governed by the indicated linear inequalities. (Bottom) A polygon in 2D genome space expresses the linear dependency between breakpoints
to lie within the indicated orange blocks, and are governed by the indicated linear inequalities. (Bottom) A polygon in 2D genome space expresses the linear dependency between breakpoints  and
and  and records the uncertainty in the location of the breakpoints.
and records the uncertainty in the location of the breakpoints.
Similar articles
-
Structural variations in plant genomes.Brief Funct Genomics. 2014 Jul;13(4):296-307. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elu016. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Brief Funct Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24907366 Free PMC article.
-
Geographic distribution and adaptive significance of genomic structural variants: an anthropological genetics perspective.Hum Biol. 2014 Fall;86(4):260-75. doi: 10.13110/humanbiology.86.4.0260. Hum Biol. 2014. PMID: 25959693 Review.
-
svclassify: a method to establish benchmark structural variant calls.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jan 16;17:64. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2366-2. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26772178 Free PMC article.
-
Paired-end mapping reveals extensive structural variation in the human genome.Science. 2007 Oct 19;318(5849):420-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1149504. Epub 2007 Sep 27. Science. 2007. PMID: 17901297 Free PMC article.
-
A decade of structural variants: description, history and methods to detect structural variation.Brief Funct Genomics. 2015 Sep;14(5):305-14. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elv014. Epub 2015 Apr 15. Brief Funct Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25877305 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide analyses of LINE-LINE-mediated nonallelic homologous recombination.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Feb 27;43(4):2188-98. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1394. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25613453 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetic testing and the future of clinical genomics.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 Jun;14(6):415-26. doi: 10.1038/nrg3493. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23681062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structural basis for cancer treatment decisions.Oncotarget. 2014 Sep 15;5(17):7285-302. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2439. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25277176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrent PTPRT/JAK2 mutations in lung adenocarcinoma among African Americans.Nat Commun. 2019 Dec 16;10(1):5735. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13732-y. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31844068 Free PMC article.
-
High dynamism for neo-sex chromosomes: satellite DNAs reveal complex evolution in a grasshopper.Heredity (Edinb). 2020 Sep;125(3):124-137. doi: 10.1038/s41437-020-0327-7. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Heredity (Edinb). 2020. PMID: 32499661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stratton MR (2011) Exploring the genomes of cancer cells: progress and promise. Science 331: 1553–1558. - PubMed
-
- Sharp AJ, Cheng Z, Eichler EE (2006) Structural variation of the human genome. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 7: 407–442. - PubMed
-
- Iafrate A, Feuk L, Rivera M, Listewnik M, Donahoe P, et al. (2004) Detection of large-scale variation in the human genome. Nat Genet 36: 949–951. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

