Pathways of antigen processing
- PMID: 23298205
- PMCID: PMC4026165
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095910
Pathways of antigen processing
Abstract
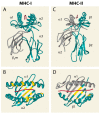
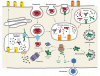
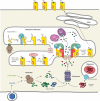
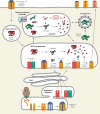
T cell recognition of antigen-presenting cells depends on their expression of a spectrum of peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) and class II (MHC-II) molecules. Conversion of antigens from pathogens or transformed cells into MHC-I- and MHC-II-bound peptides is critical for mounting protective T cell responses, and similar processing of self proteins is necessary to establish and maintain tolerance. Cells use a variety of mechanisms to acquire protein antigens, from translation in the cytosol to variations on the theme of endocytosis, and to degrade them once acquired. In this review, we highlight the aspects of MHC-I and MHC-II biosynthesis and assembly that have evolved to intersect these pathways and sample the peptides that are produced.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex molecules.Peptides. 1998;19(1):179-98. doi: 10.1016/s0196-9781(97)00277-5. Peptides. 1998. PMID: 9437752 Review.
-
Alternate class I MHC antigen processing is inhibited by Toll-like receptor signaling pathogen-associated molecular patterns: Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kDa lipoprotein, CpG DNA, and lipopolysaccharide.J Immunol. 2003 Aug 1;171(3):1413-22. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.3.1413. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12874233
-
Class II MHC/peptide complexes are released from APC and are acquired by T cell responders during specific antigen recognition.J Immunol. 1999 Nov 15;163(10):5201-10. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10553040
-
Contrasting efficacy of presentation by major histocompatibility complex class I and class II products when peptides are administered within a common protein carrier, self immunoglobulin.Eur J Immunol. 1993 Nov;23(11):2746-50. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231104. Eur J Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8223850
-
Autophagy and its role in MHC-mediated antigen presentation.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3335-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803458. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19265109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neoantigen vaccine platforms in clinical development: understanding the future of personalized immunotherapy.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021 May;30(5):529-541. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2021.1896702. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33641576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD8+ T cell clonotypes from prior SARS-CoV-2 infection predominate during the cellular immune response to mRNA vaccination.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2022 Oct 10:rs.3.rs-2146712. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2146712/v1. Res Sq. 2022. PMID: 36263073 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Modulating the microenvironment during FVIII uptake influences the nature of FVIII-peptides presented by antigen-presenting cells.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 21;13:975680. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975680. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389737 Free PMC article.
-
Production of soluble pMHC-I molecules in mammalian cells using the molecular chaperone TAPBPR.Protein Eng Des Sel. 2019 Dec 31;32(12):525-532. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzaa015. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2019. PMID: 32725167 Free PMC article.
-
A novel RNAseq-assisted method for MHC class I genotyping in a non-model species applied to a lethal vaccination-induced alloimmune disease.BMC Genomics. 2016 May 17;17:365. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2688-0. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27188848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen NR, Garg S, Brenner MB. Antigen Presentation by CD1 Lipids, T Cells, and NKT Cells in Microbial Immunity. Adv Immunol. 2009;102:1–94. - PubMed
-
- Adams E. Biology and Structure of Nonclassical MHC Class I Molecules. Ann Rev. Immunol. 2013 in press. - PubMed
-
- Watts C. The exogenous pathway for antigen presentation on major histocompatibility complex class II and CD1 molecules. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:685–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI059167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI097206/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01AI069085/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01DK085505/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI049589/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI059167/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI079065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI056097/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI069085/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI097206/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI079065/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI084853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01AI084853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

