Protein phosphatase 1 inhibits p53 signaling by dephosphorylating and stabilizing Mdmx
- PMID: 23277204
- PMCID: PMC3595384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.12.014
Protein phosphatase 1 inhibits p53 signaling by dephosphorylating and stabilizing Mdmx
Abstract
The activation and stabilization of the p53 protein play a major role in the DNA damage response. Protein levels of p53 are tightly controlled by transcriptional regulation and a number of positive and negative posttranslational modifiers, including kinases, phosphatases, E3 ubiquitin ligases, deubiquitinases, acetylases and deacetylases. One of the primary p53 regulators is Mdmx. Despite its RING domain and structural similarity with Mdm2, Mdmx does not have an intrinsic ligase activity, but inhibits the transcriptional activity of p53. Previous studies reported that Mdmx is phosphorylated and destabilized in response to DNA damage stress. Three phosphorylation sites identified are Ser342, Ser367, and Ser403. In the present study, we identify protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) as a negative regulator in the p53 signaling pathway. PP1 directly interacts with Mdmx and specifically dephosphorylates Mdmx at Ser367. The dephosphorylation of Mdmx increases its stability and thereby inhibits p53 activity. Our results suggest that PP1 is a crucial component in the ATM-Chk2-p53 signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

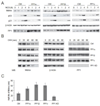
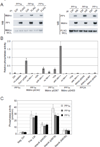
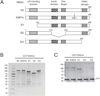


Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation and degradation of MdmX is inhibited by Wip1 phosphatase in the DNA damage response.Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 15;69(20):7960-8. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0634. Epub 2009 Oct 6. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19808970 Free PMC article.
-
ATM and Chk2-dependent phosphorylation of MDMX contribute to p53 activation after DNA damage.EMBO J. 2005 Oct 5;24(19):3411-22. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600812. Epub 2005 Sep 15. EMBO J. 2005. PMID: 16163388 Free PMC article.
-
ATM-mediated phosphorylations inhibit Mdmx/Mdm2 stabilization by HAUSP in favor of p53 activation.Cell Cycle. 2005 Sep;4(9):1166-70. doi: 10.4161/cc.4.9.1981. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Cell Cycle. 2005. PMID: 16082221 Review.
-
MdmX is required for p53 interaction with and full induction of the Mdm2 promoter after cellular stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Apr;32(7):1214-25. doi: 10.1128/MCB.06150-11. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22290440 Free PMC article.
-
Mdm2 and MdmX partner to regulate p53.FEBS Lett. 2012 May 21;586(10):1390-6. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.02.049. Epub 2012 Mar 8. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22673503 Review.
Cited by
-
Phosphatases reverse p53-mediated cell cycle checkpoints.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 May 20;111(20):7172-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1405663111. Epub 2014 May 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24808140 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Large-Scale Analysis of CRISPR/Cas9 Cell-Cycle Knockouts Reveals the Diversity of p53-Dependent Responses to Cell-Cycle Defects.Dev Cell. 2017 Feb 27;40(4):405-420.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.01.012. Epub 2017 Feb 16. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28216383 Free PMC article.
-
Scalable Nonparametric Prescreening Method for Searching Higher-Order Genetic Interactions Underlying Quantitative Traits.Genetics. 2019 Dec;213(4):1209-1224. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302658. Epub 2019 Oct 4. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31585953 Free PMC article.
-
Kinin B1 receptor and TLR4 interaction in inflammatory response.Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep;73(9):1459-1476. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01909-1. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38965133
-
Overexpression of Protein Phosphatase 1γ (PP1γ) Is Associated with Enhanced Cell Proliferation and Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Jan;62(1):133-142. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4365-1. Epub 2016 Dec 5. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 27921263
References
-
- Appella E, Anderson CW. Signaling to p53: breaking the posttranslational modification code. Pathol. Biol. (Paris) 2000;48:227–245. - PubMed
-
- Toledo F, Wahl GM. Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:909–923. - PubMed
-
- Benard J, Douc-Rasy S, Ahomadegbe JC. TP53 family members and human cancers. Hum. Mutat. 2003;21:182–191. - PubMed
-
- Marine JC, Dyer MA, Jochemsen AG. MDMX: from bench to bedside. J. Cell Sci. 2007;120:371–378. - PubMed
-
- Toledo F, Wahl GM. Regulating the p53 pathway: in vitro hypotheses, in vivo veritas. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2006;6:909–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

