Discovery of STL polyomavirus, a polyomavirus of ancestral recombinant origin that encodes a unique T antigen by alternative splicing
- PMID: 23276405
- PMCID: PMC3693558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.12.005
Discovery of STL polyomavirus, a polyomavirus of ancestral recombinant origin that encodes a unique T antigen by alternative splicing
Erratum in
- Virology. 2013 May 10;439(2):163-4
Abstract
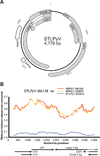
The family Polyomaviridae is comprised of circular double-stranded DNA viruses, several of which are associated with diseases, including cancer, in immunocompromised patients. Here we describe a novel polyomavirus recovered from the fecal microbiota of a child in Malawi, provisionally named STL polyomavirus (STLPyV). We detected STLPyV in clinical stool specimens from USA and The Gambia at up to 1% frequency. Complete genome comparisons of two STLPyV strains demonstrated 5.2% nucleotide divergence. Alternative splicing of the STLPyV early region yielded a unique form of T antigen, which we named 229T, in addition to the expected large and small T antigens. STLPyV has a mosaic genome and shares an ancestral recombinant origin with MWPyV. The discovery of STLPyV highlights a novel alternative splicing strategy and advances our understanding of the complex evolutionary history of polyomaviruses.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The prevalence of STL polyomavirus in stool samples from Chinese children.J Clin Virol. 2015 May;66:19-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.02.017. Epub 2015 Feb 26. J Clin Virol. 2015. PMID: 25866330
-
DNA and seroprevalence study of MW and STL polyomaviruses.J Med Virol. 2024 Aug;96(8):e29860. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29860. J Med Virol. 2024. PMID: 39145597
-
[New, newer, newest human polyomaviruses: how far?].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2013 Apr;47(2):362-81. doi: 10.5578/mb.5377. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2013. PMID: 23621738 Review. Turkish.
-
Identification of MW polyomavirus, a novel polyomavirus in human stool.J Virol. 2012 Oct;86(19):10321-6. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01210-12. Epub 2012 Jun 27. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22740408 Free PMC article.
-
Genome analysis of the new human polyomaviruses.Rev Med Virol. 2012 Nov;22(6):354-77. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1711. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Rev Med Virol. 2012. PMID: 22461085 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection Analysis and Study of Genomic Region Variability of JCPyV, BKPyV, MCPyV, HPyV6, HPyV7 and QPyV in the Urine and Plasma of HIV-1-Infected Patients.Viruses. 2022 Nov 17;14(11):2544. doi: 10.3390/v14112544. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36423152 Free PMC article.
-
Novel polyomaviruses of nonhuman primates: genetic and serological predictors for the existence of multiple unknown polyomaviruses within the human population.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(6):e1003429. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003429. Epub 2013 Jun 20. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23818846 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
JC viruria and kidney disease in APOL1 risk genotype individuals: is this a clue to a gene × environment interaction?Kidney Int. 2013 Dec;84(6):1069-72. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.299. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 24280748 Free PMC article.
-
Retrospective use of next-generation sequencing reveals the presence of Enteroviruses in acute influenza-like illness respiratory samples collected in South/South-East Asia during 2010-2013.J Clin Virol. 2017 Sep;94:91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 14. J Clin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28779659 Free PMC article.
-
Human polyomavirus type six in respiratory samples from hospitalized children with respiratory tract infections in Beijing, China.Virol J. 2015 Oct 13;12:166. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0390-5. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 26463646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babakir-Mina M, Ciccozzi M, Perno CF, Ciotti M. The novel KI, WU, MC polyomaviruses: possible human pathogens? New Microbiol. 2011;34:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharjee S. Evolutionary interrelationships among polyomaviruses based on nucleotide and amino acid variations. Indian Journal of Biotechnology. 2010;9:252–264.
-
- Bialasiewicz S, Rockett R, Whiley DW, Abed Y, Allander T, Binks M, Boivin G, Cheng AC, Chung JY, Ferguson PE, Gilroy NM, Leach AJ, Lindau C, Rossen JW, Sorrell TC, Nissen MD, Sloots TP. Whole-genome characterization and genotyping of global WU polyomavirus strains. J Virol. 2010;84:6229–6234. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

