Inflammatory markers and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 23264288
- PMCID: PMC3526249
- DOI: 10.2337/dc12-0702
Inflammatory markers and risk of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: There has been growing evidence that inflammatory markers play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes. We aimed to systematically review prospective studies on the associations of elevated levels of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and C-reactive protein (CRP) with increased risk of type 2 diabetes by conducting a meta-analysis.
Research design and methods: A systematic search of the PubMed, EMBASE, ISI Web of Knowledge, and Cochrane Library databases up until 10 February 2012 was conducted to retrieve prospective studies matched to search terms. We used generalized least-squares trend estimation to assess dose-response relationships. The summary risk estimates were pooled using either fixed-effects or random-effects models to incorporate between-study variation.
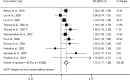
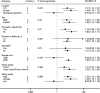
Results: The meta-analysis, including 10 prospective studies, with a total of 19,709 participants and 4,480 cases, detected a significant dose-response association of IL-6 levels with type 2 diabetes risk (relative risk [RR] 1.31 [95% CI 1.17-1.46]). For CRP, the meta-analysis involving 22 cohorts, with a total of 40,735 participants and 5,753 cases, showed that elevated CRP levels were significantly associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes (1.26 [1.16-1.37]), with the absence of publication bias. Sensitivity and subgroup analyses further supported the associations.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis provides further evidence that elevated levels of IL-6 and CRP are significantly associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cytokine. 2016 Oct;86:100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2016.06.028. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Cytokine. 2016. PMID: 27498215 Review.
-
Inflammatory Markers of CRP, IL6, TNFα, and Soluble TNFR2 and the Risk of Ovarian Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Prospective Studies.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016 Aug;25(8):1231-9. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-16-0120. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2016. PMID: 27277846
-
The effect of resveratrol supplementation on C-reactive protein (CRP) in type 2 diabetic patients: Results from a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2020 Mar;49:102251. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.102251. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Complement Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32147058
-
C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus.JAMA. 2001 Jul 18;286(3):327-34. doi: 10.1001/jama.286.3.327. JAMA. 2001. PMID: 11466099 Clinical Trial.
-
What is the impact of n-3 PUFAs on inflammation markers in Type 2 diabetic mellitus populations?: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Aug 20;15:133. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0303-7. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27544079 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D Levels Decline with Rising Number of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Healthy Adults: Association with Adipokines, Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Advanced Glycation Markers.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 29;10(6):e0131753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131753. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26120828 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of long-term trajectories of depression for incident diabetes mellitus in patients with stable coronary heart disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 May 13;20(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01298-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33985516 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating levels of DDIT4 and mTOR, and contributions of BMI, inflammation and insulin sensitivity in hyperlipidemia.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Sep 8;24(5):666. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11602. eCollection 2022 Nov. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36168416 Free PMC article.
-
Mediterranean diet for type 2 diabetes: cardiometabolic benefits.Endocrine. 2017 Apr;56(1):27-32. doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-1018-2. Epub 2016 Jul 9. Endocrine. 2017. PMID: 27395419
-
DPP4/CD32b/NF-κB Circuit: A Novel Druggable Target for Inhibiting CRP-Driven Diabetic Nephropathy.Mol Ther. 2021 Jan 6;29(1):365-375. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.08.017. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 32956626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1047–1053 - PubMed
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes 2011;29:116–122
-
- Donath MY, Shoelson SE. Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2011;11:98–107 - PubMed
-
- Doi Y, Kiyohara Y, Kubo M, et al. Elevated C-reactive protein is a predictor of the development of diabetes in a general Japanese population: the Hisayama Study. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2497–2500 - PubMed
-
- Pradhan AD, Manson JE, Rifai N, Buring JE, Ridker PM. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2001;286:327–334 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

