Genome-wide identification of enhancers in skeletal muscle: the role of MyoD1
- PMID: 23249738
- PMCID: PMC3533080
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.200113.112
Genome-wide identification of enhancers in skeletal muscle: the role of MyoD1
Abstract
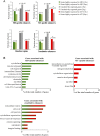
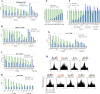
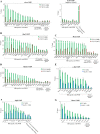
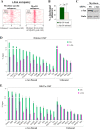
To identify the compendium of distal regulatory elements that govern myogenic differentiation, we generated chromatin state maps based on histone modifications and recruitment of factors that typify enhancers in myoblasts and myotubes. We found a striking concordance between the locations of these newly defined enhancers, MyoD1-binding events, and noncoding RNA transcripts. These enhancers recruit several sequence-specific transcription factors in a spatially constrained manner around MyoD1-binding sites. Remarkably, MyoD1-null myoblasts show a wholesale loss of recruitment of these factors as well as diminished monomethylation of H3K4 (H3K4me1) and acetylation of H3K27 (H3K27ac) and reduced recruitment of Set7, an H3K4 monomethylase. Surprisingly, we found that H3K4me1, but not H3K27ac, could be restored by re-expression of MyoD1 in MyoD1(-/-) myoblasts, although re-expression of this factor in MyoD1-null myotubes restored both histone modifications. Our studies identified a role for MyoD1 in condition-specific enhancer assembly through recruitment of transcription factors and histone-modifying enzymes that shape muscle differentiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role of MyoD1 and histone modifications in the activation of muscle enhancers.Epigenetics. 2013 Aug;8(8):778-84. doi: 10.4161/epi.25441. Epub 2013 Jun 27. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23880568 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of muscle enhancers by MyoD and epigenetic modifiers.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Nov;115(11):1855-67. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24854. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24905980 Free PMC article.
-
Myogenin is required for assembly of the transcription machinery on muscle genes during skeletal muscle differentiation.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 19;16(1):e0245618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245618. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33465133 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle programming and re-programming.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Oct;23(5):568-73. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23756045 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The MyoD family of transcription factors and skeletal myogenesis.Bioessays. 1995 Mar;17(3):203-9. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170306. Bioessays. 1995. PMID: 7748174 Review.
Cited by
-
Myogenesis defects in a patient-derived iPSC model of hereditary GNE myopathy.NPJ Regen Med. 2022 Sep 9;7(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s41536-022-00238-3. NPJ Regen Med. 2022. PMID: 36085325 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional regulation by the Set7 lysine methyltransferase.Epigenetics. 2013 Apr;8(4):361-72. doi: 10.4161/epi.24234. Epub 2013 Mar 11. Epigenetics. 2013. PMID: 23478572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loci-specific histone acetylation profiles associated with transcriptional coactivator p300 during early myoblast differentiation.Epigenetics. 2018;13(6):642-654. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2018.1489659. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 29927685 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin and transcription factor profiling in rare stem cell populations using CUT&Tag.STAR Protoc. 2021 Aug 19;2(3):100751. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100751. eCollection 2021 Sep 17. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34467227 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue-specific epigenetics in gene neighborhoods: myogenic transcription factor genes.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Aug 15;24(16):4660-73. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv198. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26041816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bengal E, Ransone L, Scharfmann R, Dwarki VJ, Tapscott SJ, Weintraub H, Verma IM 1992. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: A direct physical association. Cell 68: 507–519 - PubMed
-
- Blackwood EM, Kadonaga JT 1998. Going the distance: A current view of enhancer action. Science 281: 60–63 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
