Development and validation of a Q-PCR based TCID50 method for human herpesvirus 6
- PMID: 23249654
- PMCID: PMC3546908
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-9-311
Development and validation of a Q-PCR based TCID50 method for human herpesvirus 6
Abstract
Background: For titer assessment of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), IFA targeting viral proteins or a TCID(50) method with ocular inspection for CPE can be used. These methods rely on the subjective decision of the assessor, obstructing the ability to obtain unanimous results.
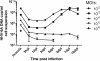
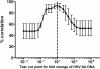
Findings: We have developed and validated an alternative TCID(50) read-out approach where infection in the titration culture plate is assessed by viral DNA load change by quantitative PCR. A ten time increase in viral DNA load was determined as cut point for infection since that yielded a maximum correlation with viral protein expression (93%). The average intra-assay CV was 9% for quantitative PCR read-out of TCID(50) compared to 45% for ocular inspection read-out of TCID(50) , 14% for IFA read-out of TCID(50), and 43% for an infectious units approach using IFA. The average inter-assay CV for quantitative PCR read-out of TCID(50) was 73%, compared to 66%, 25% and 77% for the ocular inspection read-out for TCID(50), IFA read-out of TCID(50)and infectious unit approaches respectively.
Conclusions: The quantitative PCR based read-out of TCID(50)proved to be more robust and easier to interpret than traditional TCID(50)assessment approaches for HHV-6, and therefore it might be considered as an alternative method.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of a laboratory developed real-time PCR assay and the RealStar® HHV-6 PCR Kit for quantitative detection of human herpesvirus 6.J Virol Methods. 2017 Aug;246:112-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 2. J Virol Methods. 2017. PMID: 28476346
-
Quantitation of human herpesvirus 6 DNA in infant with exanthem subitum by microplate PCR-hybridization assay.Pediatr Int. 2001 Aug;43(4):372-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1442-200x.2001.01401.x. Pediatr Int. 2001. PMID: 11472582
-
Differential tropism of human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) variants and induction of latency by HHV-6A in oligodendrocytes.J Neurovirol. 2005 Aug;11(4):384-94. doi: 10.1080/13550280591002379. J Neurovirol. 2005. PMID: 16162481 Free PMC article.
-
A multiplex real-time PCR quantitation of human herpesvirus-6, 7, 8 viruses: application in blood transfusions.Virol J. 2021 Feb 18;18(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01510-6. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 33602271 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of two viral transcripts by real time PCR to investigate human herpesvirus type 6 active infection.J Clin Virol. 2014 Feb;59(2):94-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2013.11.014. Epub 2013 Dec 7. J Clin Virol. 2014. PMID: 24380721
Cited by
-
Human herpesvirus 6A partially suppresses functional properties of DC without viral replication.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058122. Epub 2013 Mar 5. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23526966 Free PMC article.
-
In Vivo Characterisation of Five Strains of Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus 1 (Subgenotype 1c).Pathogens. 2018 Jan 19;7(1):12. doi: 10.3390/pathogens7010012. Pathogens. 2018. PMID: 29351201 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of UV-C dose and SARS-CoV-2 viral inactivation across N95 respirators during decontamination.Sci Rep. 2021 Oct 13;11(1):20341. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98121-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34645859 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical Sensitivity Comparison between Singleplex Real-Time PCR and a Multiplex PCR Platform for Detecting Respiratory Viruses.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 16;10(11):e0143164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143164. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26569120 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):599-608. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10387. Epub 2019 May 21. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reed LJ, Muench H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoint. Am J Hyg. 1938;27:493–497.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

