Chromosome 19 annotations with disease speciation: a first report from the Global Research Consortium
- PMID: 23249167
- PMCID: PMC3539432
- DOI: 10.1021/pr3008607
Chromosome 19 annotations with disease speciation: a first report from the Global Research Consortium
Abstract
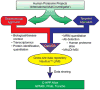
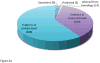
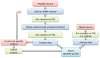
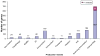
A first research development progress report of the Chromosome 19 Consortium with members from Sweden, Norway, Spain, United States, China and India, a part of the Chromosome-centric Human Proteome Project (C-HPP) global initiative, is presented ( http://www.c-hpp.org ). From the chromosome 19 peptide-targeted library constituting 6159 peptides, a pilot study was conducted using a subset with 125 isotope-labeled peptides. We applied an annotation strategy with triple quadrupole, ESI-Qtrap, and MALDI mass spectrometry platforms, comparing the quality of data within and in between these instrumental set-ups. LC-MS conditions were outlined by multiplex assay developments, followed by MRM assay developments. SRM was applied to biobank samples, quantifying kallikrein 3 (prostate specific antigen) in plasma from prostate cancer patients. The antibody production has been initiated for more than 1200 genes from the entire chromosome 19, and the progress developments are presented. We developed a dedicated transcript microarray to serve as the mRNA identifier by screening cancer cell lines. NAPPA protein arrays were built to align with the transcript data with the Chromosome 19 NAPPA chip, dedicated to 90 proteins, as the first development delivery. We have introduced an IT-infrastructure utilizing a LIMS system that serves as the key interface for the research teams to share and explore data generated within the project. The cross-site data repository will form the basis for sample processing, including biological samples as well as patient samples from national Biobanks.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Hans Lilja holds patents for free PSA, intact PSA, and hK2 assays.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Spanish human proteome project: dissection of chromosome 16.J Proteome Res. 2013 Jan 4;12(1):112-22. doi: 10.1021/pr300898u. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 23234512
-
Identification of missing proteins in the neXtProt database and unregistered phosphopeptides in the PhosphoSitePlus database as part of the Chromosome-centric Human Proteome Project.J Proteome Res. 2013 Jun 7;12(6):2414-21. doi: 10.1021/pr300825v. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 23312004
-
RNA- and antibody-based profiling of the human proteome with focus on chromosome 19.J Proteome Res. 2014 Apr 4;13(4):2019-27. doi: 10.1021/pr401156g. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Proteome Res. 2014. PMID: 24579871
-
Proteogenomics in the context of the Human Proteome Project (HPP).Expert Rev Proteomics. 2019 Mar;16(3):267-275. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2019.1571916. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30654666 Review.
-
Advances in the Chromosome-Centric Human Proteome Project: looking to the future.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017 Dec;14(12):1059-1071. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2017.1394189. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 29039980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide barcodes in dogs affected by mitral valve disease with and without pulmonary hypertension using MALDI-TOF MS and LC-MS/MS.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 12;16(8):e0255611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255611. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34383793 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-automated biobank sample processing with a 384 high density sample tube robot used in cancer and cardiovascular studies.Clin Transl Med. 2015 Dec;4(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s40169-015-0067-0. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Clin Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26272727 Free PMC article.
-
Large Scale Identification of Variant Proteins in Glioma Stem Cells.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jan 17;9(1):73-79. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00362. Epub 2017 Dec 21. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29254333 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Transcriptomic and Glycomic Profiling of Glioma Stem Cell Xenografts.J Proteome Res. 2015 Sep 4;14(9):3932-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00549. Epub 2015 Aug 4. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 26185906 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic identification of single amino acid variants in glioma stem-cell-derived chromosome 19 proteins.J Proteome Res. 2015 Feb 6;14(2):778-86. doi: 10.1021/pr500810g. Epub 2014 Nov 25. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 25399873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hancock W, Omenn G, Legrain P, Paik YK. Proteomics, Human Proteome Project, and Chromosomes. J Proteome Res. 2011;10(1):210–210. - PubMed
-
- Legrain P, Aebersold R, Archakov A, Bairoch A, Bala K, Beretta L, Bergeron J, Borchers CH, Corthals GL, Costello CE, Deutsch EW, Domon B, Hancock W, He FC, Hochstrasser D, Marko-Varga G, Salekdeh GH, Sechi S, Snyder M, Srivastava S, Uhlen M, Wu CH, Yamamoto T, Paik YK, Omenn GS. The Human Proteome Project: Current State and Future Direction. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2011;10(7) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Paik YK, Jeong SK, Omenn GS, Uhlen M, Hanash S, Cho SY, Lee HJ, Na K, Choi EY, Yan FF, Zhang F, Zhang Y, Snyder M, Cheng Y, Chen R, Marko-Varga G, Deutsch EW, Kim H, Kwon JY, Aebersold R, Bairoch A, Taylor AD, Kim KY, Lee EY, Hochstrasser D, Legrain P, Hancock WS. The Chromosome-Centric Human Proteome Project for cataloging proteins encoded in the genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2012;30(3):221–223. - PubMed

