Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010
- PMID: 23245604
- PMCID: PMC10790329
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0
Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010
Erratum in
- Lancet. 2013 Feb 23;381(9867):628. AlMazroa, Mohammad A [added]; Memish, Ziad A [added]
Abstract
Background: Reliable and timely information on the leading causes of death in populations, and how these are changing, is a crucial input into health policy debates. In the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study 2010 (GBD 2010), we aimed to estimate annual deaths for the world and 21 regions between 1980 and 2010 for 235 causes, with uncertainty intervals (UIs), separately by age and sex.
Methods: We attempted to identify all available data on causes of death for 187 countries from 1980 to 2010 from vital registration, verbal autopsy, mortality surveillance, censuses, surveys, hospitals, police records, and mortuaries. We assessed data quality for completeness, diagnostic accuracy, missing data, stochastic variations, and probable causes of death. We applied six different modelling strategies to estimate cause-specific mortality trends depending on the strength of the data. For 133 causes and three special aggregates we used the Cause of Death Ensemble model (CODEm) approach, which uses four families of statistical models testing a large set of different models using different permutations of covariates. Model ensembles were developed from these component models. We assessed model performance with rigorous out-of-sample testing of prediction error and the validity of 95% UIs. For 13 causes with low observed numbers of deaths, we developed negative binomial models with plausible covariates. For 27 causes for which death is rare, we modelled the higher level cause in the cause hierarchy of the GBD 2010 and then allocated deaths across component causes proportionately, estimated from all available data in the database. For selected causes (African trypanosomiasis, congenital syphilis, whooping cough, measles, typhoid and parathyroid, leishmaniasis, acute hepatitis E, and HIV/AIDS), we used natural history models based on information on incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality. We separately estimated cause fractions by aetiology for diarrhoea, lower respiratory infections, and meningitis, as well as disaggregations by subcause for chronic kidney disease, maternal disorders, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. For deaths due to collective violence and natural disasters, we used mortality shock regressions. For every cause, we estimated 95% UIs that captured both parameter estimation uncertainty and uncertainty due to model specification where CODEm was used. We constrained cause-specific fractions within every age-sex group to sum to total mortality based on draws from the uncertainty distributions.
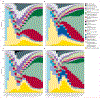
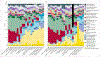
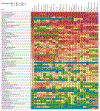
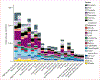
Findings: In 2010, there were 52·8 million deaths globally. At the most aggregate level, communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional causes were 24·9% of deaths worldwide in 2010, down from 15·9 million (34·1%) of 46·5 million in 1990. This decrease was largely due to decreases in mortality from diarrhoeal disease (from 2·5 to 1·4 million), lower respiratory infections (from 3·4 to 2·8 million), neonatal disorders (from 3·1 to 2·2 million), measles (from 0·63 to 0·13 million), and tetanus (from 0·27 to 0·06 million). Deaths from HIV/AIDS increased from 0·30 million in 1990 to 1·5 million in 2010, reaching a peak of 1·7 million in 2006. Malaria mortality also rose by an estimated 19·9% since 1990 to 1·17 million deaths in 2010. Tuberculosis killed 1·2 million people in 2010. Deaths from non-communicable diseases rose by just under 8 million between 1990 and 2010, accounting for two of every three deaths (34·5 million) worldwide by 2010. 8 million people died from cancer in 2010, 38% more than two decades ago; of these, 1·5 million (19%) were from trachea, bronchus, and lung cancer. Ischaemic heart disease and stroke collectively killed 12·9 million people in 2010, or one in four deaths worldwide, compared with one in five in 1990; 1·3 million deaths were due to diabetes, twice as many as in 1990. The fraction of global deaths due to injuries (5·1 million deaths) was marginally higher in 2010 (9·6%) compared with two decades earlier (8·8%). This was driven by a 46% rise in deaths worldwide due to road traffic accidents (1·3 million in 2010) and a rise in deaths from falls. Ischaemic heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lower respiratory infections, lung cancer, and HIV/AIDS were the leading causes of death in 2010. Ischaemic heart disease, lower respiratory infections, stroke, diarrhoeal disease, malaria, and HIV/AIDS were the leading causes of years of life lost due to premature mortality (YLLs) in 2010, similar to what was estimated for 1990, except for HIV/AIDS and preterm birth complications. YLLs from lower respiratory infections and diarrhoea decreased by 45-54% since 1990; ischaemic heart disease and stroke YLLs increased by 17-28%. Regional variations in leading causes of death were substantial. Communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional causes still accounted for 76% of premature mortality in sub-Saharan Africa in 2010. Age standardised death rates from some key disorders rose (HIV/AIDS, Alzheimer's disease, diabetes mellitus, and chronic kidney disease in particular), but for most diseases, death rates fell in the past two decades; including major vascular diseases, COPD, most forms of cancer, liver cirrhosis, and maternal disorders. For other conditions, notably malaria, prostate cancer, and injuries, little change was noted.
Interpretation: Population growth, increased average age of the world's population, and largely decreasing age-specific, sex-specific, and cause-specific death rates combine to drive a broad shift from communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional causes towards non-communicable diseases. Nevertheless, communicable, maternal, neonatal, and nutritional causes remain the dominant causes of YLLs in sub-Saharan Africa. Overlaid on this general pattern of the epidemiological transition, marked regional variation exists in many causes, such as interpersonal violence, suicide, liver cancer, diabetes, cirrhosis, Chagas disease, African trypanosomiasis, melanoma, and others. Regional heterogeneity highlights the importance of sound epidemiological assessments of the causes of death on a regular basis.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
E R Dorsey has received consulting fees from Medtronic and Lundbeck and research support from Lundbeck and Prana Biotechnology. M Ezzati chaired a session and gave a talk at the World Cardiology Congress (WCC), with travel cost reimbursed by the World Heart Federation. At the WCC, he also gave a talk at a session organised by PepsiCo with no financial or other renumeration. P J Hotez reports holding several positions: Dean, National School of Tropical Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine; Director, Sabin Vaccine Institute Texas Children’s Hospital Center for Vaccine Development; and President, Sabin Vaccine Institute. He also is an inventor on several patents: 5,527,937 “Hookworm Anticoagulant”; 5,753,787 “Nucleic Acids for Ancylostoma Secreted Proteins”; 7,303,752 B2 “Hookworm vaccine”; 12/492,734 “Human Hookworm Vaccine”; 61/077,256 “Multivalent Anthelminthic Vaccine”; and PCT-20100701/0.20.5.18 “Malaria Transmission blocking vaccine”. G A Mensah is a former employee of PepsiCo. F Perez-Ruiz was an adviser for Ardea, Menarini, Novartis, and Metabolex; was a member of the Speaker’s Bureau for Menarini, Novartis; an adviser for educational issues for Savient; led an investigation grants for the Spanish Health Ministry, Hospital de Cruces Rheumatology Association; and was principal investigator in clinical trials for Ardea.
Figures

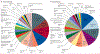


Comment in
-
Global burden of cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013 Feb;10(2):59. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2012.194. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23296068 No abstract available.
-
Mortality from HIV in the Global Burden of Disease study - authors' reply.Lancet. 2013 Mar 23;381(9871):991-2. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60704-7. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23668573 No abstract available.
-
Mortality from HIV in the Global Burden of Disease study.Lancet. 2013 Mar 23;381(9871):991. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60703-5. Epub 2013 Mar 22. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23668574 No abstract available.
-
Stroke: a global killer on the rise.World Neurosurg. 2013 Jul-Aug;80(1-2):2-4. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2013.05.002. Epub 2013 May 15. World Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23684853 No abstract available.
-
Viral hepatitis and the Global Burden of Disease: a need to regroup.J Viral Hepat. 2013 Sep;20(9):600-1. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12123. J Viral Hepat. 2013. PMID: 23910643 No abstract available.
-
On World Thrombosis Day.Lancet. 2014 Nov 8;384(9955):1653-4. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61652-4. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 25319500 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016.Lancet. 2017 Sep 16;390(10100):1151-1210. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28919116 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015.Lancet. 2016 Oct 8;388(10053):1459-1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27733281 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.Lancet. 2015 Jan 10;385(9963):117-71. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 25530442 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.Lancet. 2015 Aug 22;386(9995):743-800. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60692-4. Epub 2015 Jun 7. Lancet. 2015. PMID: 26063472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measuring the global burden of disease and epidemiological transitions: 2002-2030.Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2006 Jul-Sep;100(5-6):481-99. doi: 10.1179/136485906X97417. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16899150 Review.
Cited by
-
The burden of cirrhosis and other chronic liver disease in the middle east and North Africa (MENA) region over three decades.BMC Public Health. 2024 Oct 28;24(1):2979. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20445-5. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39468483 Free PMC article.
-
Repositioning of Antibiotics in the Treatment of Viral Infections.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Oct 26;81(12):427. doi: 10.1007/s00284-024-03948-7. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39460768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistent proteinuria is associated with the occurrence of cardiovascular disease: a nationwide population-based cohort study.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25376. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75384-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455616 Free PMC article.
-
Factor V Leiden (R506Q), Prothrombin G20210A, and MTHFR C677T Variants and Thrombophilia in Qatar Biobank Participants: A Case Control Study.Pathophysiology. 2024 Oct 21;31(4):608-620. doi: 10.3390/pathophysiology31040044. Pathophysiology. 2024. PMID: 39449526 Free PMC article.
-
An explainable machine learning estimated biological age based on morphological parameters of the spine.Geroscience. 2024 Oct 24. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01394-8. Online ahead of print. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 39446225
References
-
- Murray CJL, Kulkarni SC, Ezzati M. Understanding the coronary heart disease versus total cardiovascular mortality paradox: a method to enhance the comparability of cardiovascular death statistics in the United States. Circulation 200G; 113: 2071–81. - PubMed
-
- Ruzicka LT, Lopez AD. The use of cause-of-death statistics for health situation assessment: national and international experiences. World Health Stat Q 1990; 43: 249–58. - PubMed
-
- Lopez AD. Causes of death in the industrialized and developing countries: estimates for 1985–1990. In: Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries: Oxford Medical Publications, Oxford University Press, 1993: 15–30.
-
- Lu T-H, Shih T-P, Lee M-C, Chou M-C, Lin C-K. Diversity in death certification: a case vignette approach. J Clin Epidemiol 2001; 54: 1086–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

