FMRP targets distinct mRNA sequence elements to regulate protein expression
- PMID: 23235829
- PMCID: PMC3528815
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11737
FMRP targets distinct mRNA sequence elements to regulate protein expression
Abstract
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a multi-organ disease that leads to mental retardation, macro-orchidism in males and premature ovarian insufficiency in female carriers. FXS is also a prominent monogenic disease associated with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). FXS is typically caused by the loss of fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) expression, which codes for the RNA-binding protein FMRP. Here we report the discovery of distinct RNA-recognition elements that correspond to the two independent RNA-binding domains of FMRP, in addition to the binding sites within the messenger RNA targets for wild-type and I304N mutant FMRP isoforms and the FMRP paralogues FXR1P and FXR2P (also known as FXR1 and FXR2). RNA-recognition-element frequency, ratio and distribution determine target mRNA association with FMRP. Among highly enriched targets, we identify many genes involved in ASD and show that FMRP affects their protein levels in human cell culture, mouse ovaries and human brain. Notably, we discovered that these targets are also dysregulated in Fmr1(-/-) mouse ovaries showing signs of premature follicular overdevelopment. These results indicate that FMRP targets share signalling pathways across different cellular contexts. As the importance of signalling pathways in both FXS and ASD is becoming increasingly apparent, our results provide a ranked list of genes as basis for the pursuit of new therapeutic targets for these neurological disorders.
Figures

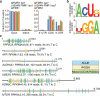

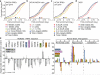

Comment in
-
Neurodevelopmental disorders: Signalling pathways of fragile X syndrome.Nature. 2012 Dec 20;492(7429):359-60. doi: 10.1038/nature11764. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Nature. 2012. PMID: 23235826 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Exaggerated behavioral phenotypes in Fmr1/Fxr2 double knockout mice reveal a functional genetic interaction between Fragile X-related proteins.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Jun 15;15(12):1984-94. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl121. Epub 2006 May 4. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16675531
-
Identification of FMRP target mRNAs in the developmental brain: FMRP might coordinate Ras/MAPK, Wnt/β-catenin, and mTOR signaling during corticogenesis.Mol Brain. 2020 Dec 16;13(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-00706-1. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 33323119 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and cellular aspects of mental retardation in the Fragile X syndrome: from gene mutation/s to spine dysmorphogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;970:517-51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-0932-8_23. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22351071 Review.
-
Expression of fragile X mental retardation-1 gene with nuclear export signal mutation changes the expression profiling of mouse cerebella immortal neuronal cell.Proteomics. 2005 Oct;5(15):3979-90. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200401252. Proteomics. 2005. PMID: 16130171
-
Increasing our understanding of human cognition through the study of Fragile X Syndrome.Dev Neurobiol. 2014 Feb;74(2):147-77. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22096. Epub 2013 Jul 30. Dev Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 23723176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genotype to phenotype relationships in autism spectrum disorders.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Feb;18(2):191-8. doi: 10.1038/nn.3907. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25531569 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2 inhibition rescues neurogenic and cognitive deficits in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.Sci Transl Med. 2016 Apr 27;8(336):336ra61. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad9370. Sci Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27122614 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal Protein Deficiencies: How Abnormal RNA Metabolism Results in Childhood-Onset Neurological Diseases.J Neuromuscul Dis. 2015;2(Suppl 2):S31-S37. doi: 10.3233/JND-150086. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2015. PMID: 27127732 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfide quinone oxidoreductase contributes to voltage sensing of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore.FASEB J. 2024 Feb 29;38(4):e23494. doi: 10.1096/fj.202301280R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38376922
-
Mechanisms coordinating ELAV/Hu mRNA regulons.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Feb;23(1):35-43. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.12.006. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 23312841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Verkerk AJ, et al. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991;65:905–914. - PubMed
-
- Kremer EJ, et al. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science (New York, N.Y. 1991;252:1711–1714. - PubMed
-
- Vincent A, et al. Abnormal pattern detected in fragile-X patients by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1991;349:624–626. - PubMed
-
- Siomi H, Siomi MC, Nussbaum RL, Dreyfuss G. The protein product of the fragile X gene, FMR1, has characteristics of an RNA-binding protein. Cell. 1993;74:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Ashley CTJ, Wilkinson KD, Reines D, Warren ST. FMR1 protein: conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science (New York, N.Y. 1993;262:563–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

