The D₁ dopamine receptor agonist, SKF83959, attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in RGC-5 cells involving the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/p38 pathways
- PMID: 23233790
- PMCID: PMC3519376
The D₁ dopamine receptor agonist, SKF83959, attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in RGC-5 cells involving the extracellular signal-regulated kinase/p38 pathways
Abstract
Purpose: Oxidative stress is widely implicated in the death of retinal ganglion cells associated with various optic neuropathies. Agonists of the dopamine D(1) receptor have recently been found to be potentially neuroprotective against oxidative stress-induced injury. The goal of this study was to investigate whether SKF83959, a next-generation high-affinity D(1) receptor agonist, could protect retinal ganglion cell 5 (RGC-5) cells from H(2)O(2)-induced damage and the molecular mechanism involved.
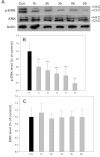
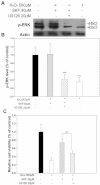
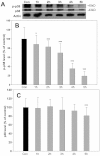
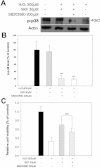
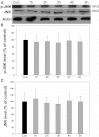
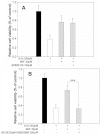
Methods: We examined expression of the D(1) receptor in RGC-5 cells with reverse-transcription-PCR and immunoblotting and assessed neuroprotection using propidium iodide staining and the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. In addition, we monitored the activation and involvement of members of mitogen-activated protein kinase family, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38 and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase, with western blot and specific inhibitors.
Results: We found that the D(1) receptor was expressed in RGC-5 cells, but the sequence analysis suggested this cell line is from mouse and not rat origin. SKF83959 exhibited a remarkable neuroprotective effect on H(2)O(2)-damaged RGC-5 cells, which was blocked by the specific D(1) receptor antagonist, SCH23390. ERK and p38 were activated by SKF83959, and pretreatment with their inhibitors U0126 and SB203580, respectively, significantly blunted the SKF83959-induced cytoprotection. However, the specific c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase inhibitor, SP600125, had no effect on the SKF83959-induced protection.
Conclusions: We conclude that SKF83959 attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced injury in RGC-5 cells via a mechanism involving activation of the ERK and p38 pathways and the D(1) receptor is a potential molecular target for developing neuroprotective drugs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of atypical D1 receptor agonist SKF83959 are mediated via D1 receptor-dependent inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta and a receptor-independent anti-oxidative action.J Neurochem. 2008 Feb;104(4):946-56. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05062.x. Epub 2007 Nov 14. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18005341
-
D1 dopamine receptor agonists mediate activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Jun amino-terminal kinase by a protein kinase A-dependent mechanism in SK-N-MC human neuroblastoma cells.Mol Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;54(3):453-8. doi: 10.1124/mol.54.3.453. Mol Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9730903
-
Endothelin-1 stimulates preadipocyte growth via the PKC, STAT3, AMPK, c-JUN, ERK, sphingosine kinase, and sphingomyelinase pathways.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov 1;319(5):C839-C857. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00491.2019. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32755450
-
Sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation in neonate 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats after repeated D1-dopamine receptor agonist administration: implications for NMDA receptor involvement.J Neurosci. 2004 Jun 30;24(26):5863-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0528-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15229233 Free PMC article.
-
SKF83959 selectively regulates phosphatidylinositol-linked D1 dopamine receptors in rat brain.J Neurochem. 2003 Apr;85(2):378-86. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01698.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12675914
Cited by
-
Expression of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors in the human retina revealed by positron emission tomography and targeted mass spectrometry.Exp Eye Res. 2018 Oct;175:32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jun 5. Exp Eye Res. 2018. PMID: 29883636 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine deficiency contributes to early visual dysfunction in a rodent model of type 1 diabetes.J Neurosci. 2014 Jan 15;34(3):726-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3483-13.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24431431 Free PMC article.
-
The effect and underlying mechanism of Timosaponin B-II on RGC-5 necroptosis induced by hydrogen peroxide.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 2;14:459. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-459. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25439561 Free PMC article.
-
Sterigmatocystin declines mouse oocyte quality by inducing ferroptosis and asymmetric division defects.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Aug 28;17(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01499-w. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 39198920 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor interacting protein 3-induced RGC-5 cell necroptosis following oxygen glucose deprivation.BMC Neurosci. 2015 Aug 4;16:49. doi: 10.1186/s12868-015-0187-x. BMC Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26238997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johns DR, Colby KA. Treatment of Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy: theory to practice. Semin Ophthalmol. 2002;17:33–8. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg-Cohen N, Dadon-Bar-El S, Hasanreisoglu M, Avraham-Lubin BC, Dratviman-Storobinsky O, Cohen Y, Weinberger D. Possible neuroprotective effect of brimonidine in a mouse model of ischaemic optic neuropathy. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2009;37:718–29. - PubMed
-
- Levkovitch-Verbin H, Harris-Cerruti C, Groner Y, Wheeler LA, Schwartz M, Yoles E. RGC death in mice after optic nerve crush injury: oxidative stress and neuroprotection. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:4169–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
