NOX2 deficiency attenuates markers of adiposopathy and brain injury induced by high-fat diet
- PMID: 23233541
- PMCID: PMC3566505
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00398.2012
NOX2 deficiency attenuates markers of adiposopathy and brain injury induced by high-fat diet
Abstract
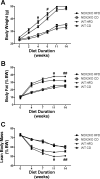
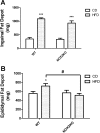
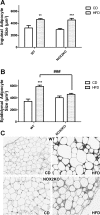
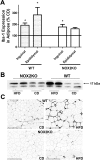
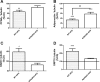
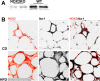
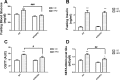
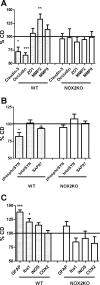
The consumption of high-fat/calorie diets in modern societies is likely a major contributor to the obesity epidemic, which can increase the prevalence of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological impairment. Obesity may precipitate decline via inflammatory and oxidative signaling, and one factor linking inflammation to oxidative stress is the proinflammatory, pro-oxidant enzyme NADPH oxidase. To reveal the role of NADPH oxidase in the metabolic and neurological consequences of obesity, the effects of high-fat diet were compared in wild-type C57Bl/6 (WT) mice and in mice deficient in the NAPDH oxidase subunit NOX2 (NOX2KO). While diet-induced weight gains in WT and NOX2KO mice were similar, NOX2KO mice had smaller visceral adipose deposits, attenuated visceral adipocyte hypertrophy, and diminished visceral adipose macrophage infiltration. Moreover, the detrimental effects of HFD on markers of adipocyte function and injury were attenuated in NOX2KO mice; NOX2KO mice had improved glucose regulation, and evaluation of NOX2 expression identified macrophages as the primary population of NOX2-positive cells in visceral adipose. Finally, brain injury was assessed using markers of cerebrovascular integrity, synaptic density, and reactive gliosis, and data show that high-fat diet disrupted marker expression in WT but not NOX2KO mice. Collectively, these data indicate that NOX2 is a significant contributor to the pathogenic effects of high-fat diet and reinforce a key role for visceral adipose inflammation in metabolic and neurological decline. Development of NOX-based therapies could accordingly preserve metabolic and neurological function in the context of metabolic syndrome.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myeloid-specific deletion of NOX2 prevents the metabolic and neurologic consequences of high fat diet.PLoS One. 2017 Aug 3;12(8):e0181500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181500. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28771483 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial roles of Nox2-derived oxidative stress in deteriorating the function of insulin receptors and endothelium in dietary obesity of middle-aged mice.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Nov;170(5):1064-77. doi: 10.1111/bph.12336. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23957783 Free PMC article.
-
Nox2 dependent redox-regulation of Akt and ERK1/2 to promote left ventricular hypertrophy in dietary obesity of mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jul 30;528(3):506-513. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.162. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32507594
-
NADPH Oxidase-2 and Atherothrombosis: Insight From Chronic Granulomatous Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Feb;37(2):218-225. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308351. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27932349 Review.
-
Adiposopathy, "sick fat," Ockham's razor, and resolution of the obesity paradox.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014 May;16(5):409. doi: 10.1007/s11883-014-0409-1. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2014. PMID: 24659222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NOX2 deficiency exacerbates diet-induced obesity and impairs molecular training adaptations in skeletal muscle.Redox Biol. 2023 Sep;65:102842. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102842. Epub 2023 Aug 6. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37572454 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in the Brain: What's New?Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 18;20(4):874. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040874. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obese-type gut microbiota induce neurobehavioral changes in the absence of obesity.Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Apr 1;77(7):607-15. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.07.012. Epub 2014 Jul 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25173628 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte-Specific Deficiency of NADPH Oxidase 4 Delays the Onset of Insulin Resistance and Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017 Mar;37(3):466-475. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308749. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28062496 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal correlation of morphological and biochemical changes with the recruitment of different mechanisms of reactive oxygen species formation during human SW872 cell adipogenic differentiation.Biofactors. 2021 Sep;47(5):837-851. doi: 10.1002/biof.1769. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Biofactors. 2021. PMID: 34260117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed Z, Shaw G, Sharma VP, Yang C, McGowan E, Dickson DW. Actin-binding proteins coronin-1a and IBA-1 are effective microglial markers for immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 55: 687–700, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H, Barger S, Barnum S, Bradt B, Bauer J, Cole G, Cooper NR, Eikelenboom P, Emmerling M, Fiebich BL, Finch CE, Frautschy S, Griffin WS, Hampel H, Hull M, Landreth G, Lue L, Mrak R, Mackenzie IR, McGeer PL, O'Banion MK, Pachter J, Pasinetti G, Plata-Salaman C, Rogers J, Rydel R, Shen Y, Streit W, Strohmeyer R, Tooyoma I, Van Muiswinkel FL, Veerhuis R, Walker D, Webster S, Wegrzyniak B, Wenk G, Wyss-Coray T. Inflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 21: 383–421, 2000 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

