Ovarian cancer : making its own rules-again
- PMID: 23233093
- PMCID: PMC3553273
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.27833
Ovarian cancer : making its own rules-again
Abstract
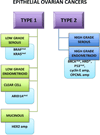
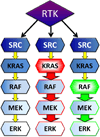
Epithelial ovarian cancer, once categorizing all epithelial cancers of the ovary and fallopian tube, is now recognized to be an umbrella term. We are recognizing two categories of ovarian cancer, with the “type 1” cancers containing further types, including low grade serous cancers, mucinous, clear cell, and low grade endometrioid. These types are genetically and histologically as different as is their outcome. The paper accompanying this editorial further dissects low grade serous cancers to show that those carrying oncogenic KRAS or BRAF mutations have an unexpectedly excellent clinical outcome. We discuss this newest unexpected behavior of ovarian cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Molecular signatures in ovarian carcinoma].Praxis (Bern 1994). 2005 Oct 5;94(40):1561-3. doi: 10.1024/0369-8394.94.40.1561. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2005. PMID: 16245918 German. No abstract available.
-
[Genetic abnormalities in the pathogenesis of ovarian cancer].Nihon Rinsho. 2012 Jun;70 Suppl 4:480-7. Nihon Rinsho. 2012. PMID: 23156294 Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Modelling genetic and clinical heterogeneity in epithelial ovarian cancers.Carcinogenesis. 2011 Oct;32(10):1540-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr140. Epub 2011 Aug 22. Carcinogenesis. 2011. PMID: 21859834
-
Low Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma: from the molecular characterization to the best therapeutic strategy.Cancer Treat Rev. 2015 Feb;41(2):136-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2014.12.003. Epub 2014 Dec 23. Cancer Treat Rev. 2015. PMID: 25573350 Review.
-
Ovarian cancer as a genetic disease.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jan 1;18(2):543-63. doi: 10.2741/4119. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23276941 Review.
Cited by
-
Ambivalent role of pFAK-Y397 in serous ovarian cancer--a study of the OVCAD consortium.Mol Cancer. 2014 Mar 21;13:67. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-67. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24655477 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 expression in epithelial ovarian cancer: effect on cell EMT and clinical outcome.Med Oncol. 2015 Feb;32(2):329. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0329-5. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Med Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25585684
-
Clinical implications of using molecular diagnostics for ovarian cancers.Ann Oncol. 2013 Dec;24 Suppl 10(Suppl 10):x22-26. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt464. Ann Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24265398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of miR-200a in mammalian epithelial cell transformation.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jan;36(1):2-12. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu202. Epub 2014 Sep 19. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 25239643 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity of the Genetic Background of Oncogenesis in Ovarian Cancer-Genetic Instability and Clinical Implications.Cells. 2024 Feb 15;13(4):345. doi: 10.3390/cells13040345. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38391958 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

