Quantifying Argonaute proteins in and out of GW/P-bodies: implications in microRNA activities
- PMID: 23224970
- PMCID: PMC3893129
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_10
Quantifying Argonaute proteins in and out of GW/P-bodies: implications in microRNA activities
Abstract
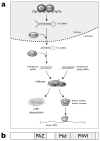
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of ∼22nt non-coding RNAs that regulate the translational potential and stability of mRNAs. Though constituting only 1-4% of human genes, miRNAs are predicted to regulate more than 60% of all mRNAs. The action of miRNAs is mediated through their associations with Argonaute proteins and mRNA targets. Previous studies indicated that though the majority of Argonaute proteins is diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm, a small fraction is consistently observed to be concentrated in a cytoplasmic compartment called GW/P-bodies. In this chapter, we will provide a quantitative and dynamic view of the subcellular localization of miRNA function, followed by a discussion on the possible roles of PBs in miRNA silencing.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Function of GW182 and GW bodies in siRNA and miRNA pathways.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:71-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224966 Review.
-
The role of GW182 proteins in miRNA-mediated gene silencing.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:147-63. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224969 Review.
-
Reflections on ten years of history of, and future prospects for, GW182 and GW/P body research.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;768:261-70. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_15. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23224975 Review. No abstract available.
-
RIP-Chip analysis supports different roles for AGO2 and GW182 proteins in recruiting and processing microRNA targets.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 18;20(Suppl 4):120. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2683-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30999843 Free PMC article.
-
Dcp1a and GW182 Induce Distinct Cellular Aggregates and Have Different Effects on microRNA Pathway.DNA Cell Biol. 2017 Jul;36(7):565-570. doi: 10.1089/dna.2017.3633. Epub 2017 May 10. DNA Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28488892
Cited by
-
Intracytoplasmic Re-localization of miRISC Complexes.Front Genet. 2018 Sep 20;9:403. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00403. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30298086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress granules and cell signaling: more than just a passing phase?Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 Oct;38(10):494-506. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 24029419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
27-Hydroxycholesterol Induces Aberrant Morphology and Synaptic Dysfunction in Hippocampal Neurons.Cereb Cortex. 2019 Jan 1;29(1):429-446. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhy274. Cereb Cortex. 2019. PMID: 30395175 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse transposable element landscapes in pathogenic and nonpathogenic yeast models: the value of a comparative perspective.Mob DNA. 2020 Apr 21;11:16. doi: 10.1186/s13100-020-00215-x. eCollection 2020. Mob DNA. 2020. PMID: 32336995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-501-3p mediates the activity-dependent regulation of the expression of AMPA receptor subunit GluA1.J Cell Biol. 2015 Mar 30;208(7):949-59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201404092. Epub 2015 Mar 23. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25800054 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

