Nervous system regulation of the cancer genome
- PMID: 23207104
- PMCID: PMC3600385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2012.11.008
Nervous system regulation of the cancer genome
Abstract
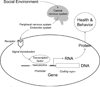
Genomics-based analyses have provided deep insight into the basic biology of cancer and are now clarifying the molecular pathways by which psychological and social factors can regulate tumor cell gene expression and genome evolution. This review summarizes basic and clinical research on neural and endocrine regulation of the cancer genome and its interactions with the surrounding tumor microenvironment, including the specific types of genes subject to neural and endocrine regulation, the signal transduction pathways that mediate such effects, and therapeutic approaches that might be deployed to mitigate their impact. Beta-adrenergic signaling from the sympathetic nervous system has been found to up-regulated a diverse array of genes that contribute to tumor progression and metastasis, whereas glucocorticoid-regulated genes can inhibit DNA repair and promote cancer cell survival and resistance to chemotherapy. Relationships between socio-environmental risk factors, neural and endocrine signaling to the tumor microenvironment, and transcriptional responses by cancer cells and surrounding stromal cells are providing new mechanistic insights into the social epidemiology of cancer, new therapeutic approaches for protecting the health of cancer patients, and new molecular biomarkers for assessing the impact of behavioral and pharmacologic interventions.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of the hypoxic tumor microenvironment on the regulation of cancer stem cell characteristics.Cancer Biol Ther. 2010 Jun 15;9(12):949-56. doi: 10.4161/cbt.9.12.12347. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010. PMID: 20581454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Notch Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancer Cell. 2018 Oct 8;34(4):536-548. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Cancer Cell. 2018. PMID: 30146333 Review.
-
Neurobiology of Cancer: the Role of β-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling in Various Tumor Environments.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 26;21(21):7958. doi: 10.3390/ijms21217958. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33114769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in cancer: Small transporters with big functions.Cancer Lett. 2018 Oct 28;435:55-65. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2018.07.037. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Cancer Lett. 2018. PMID: 30071288 Review.
-
Investigation of lipid metabolism dysregulation and the effects on immune microenvironments in pan-cancer using multiple omics data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 May 1;20(Suppl 7):195. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2734-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31074374 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Tone it down: Vagal nerve activity is associated with pro-inflammatory and anti-viral factors in breast cancer - An exploratory study.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021 Apr 30;7:100057. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2021.100057. eCollection 2021 Aug. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021. PMID: 35757058 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood experiences of parenting and cancer risk at older ages: findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing (ELSA).Int J Public Health. 2018 Sep;63(7):823-832. doi: 10.1007/s00038-018-1117-3. Epub 2018 Jun 14. Int J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29947829 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Consequences of the Acute Neural-Inflammatory Stress Response in the Cancer Surgical Patient: New Findings and Perspectives.Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2016 Fall;54(4):58-71. doi: 10.1097/AIA.0000000000000111. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2016. PMID: 27648891 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Major Stressful Life Events and the Risk of Pancreatic, Head and Neck Cancers: A Case-Control Study.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 20;16(2):451. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020451. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275892 Free PMC article.
-
The circadian clock in cancer development and therapy.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;119:221-82. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-396971-2.00009-9. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23899600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amit I, Garber M, Chevrier N, Leite AP, Donner Y, Eisenhaure T, Guttman M, Grenier JK, Li W, Zuk O, Schubert LA, Birditt B, Shay T, Goren A, Zhang X, Smith Z, Deering R, McDonald RC, Cabili M, Bernstein BE, Rinn JL, Meissner A, Root DE, Hacohen N, Regev A. Unbiased reconstruction of a mammalian transcriptional network mediating pathogen responses. Science. 2009;326:257–263. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bangalore S, Kumar S, Kjeldsen SE, Makani H, Grossman E, Wetterslev J, Gupta AK, Sever PS, Gluud C, Messerli FH. Antihypertensive drugs and risk of cancer: network meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses of 324,168 participants from randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:65–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

