Src controls tumorigenesis via JNK-dependent regulation of the Hippo pathway in Drosophila
- PMID: 23196366
- PMCID: PMC3537139
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2012.185
Src controls tumorigenesis via JNK-dependent regulation of the Hippo pathway in Drosophila
Abstract
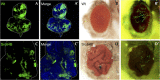
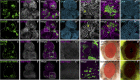
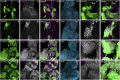
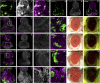
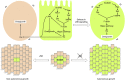
Cell-cell interactions within the tumour microenvironment have crucial roles in epithelial tumorigenesis. Using Drosophila genetics, we show that the oncoprotein Src controls tumour microenvironment by Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent regulation of the Hippo pathway. Clones of cells with elevated Src expression activate the Rac-Diaphanous and Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways, which cooperatively induce F-actin accumulation, thereby leading to activation of the Hippo pathway effector Yorkie (Yki). Simultaneously, Src activates the JNK pathway, which antagonizes the autonomous Yki activity and causes propagation of Yki activity to neighbouring cells, resulting in the overgrowth of surrounding tissue. Our data provide a mechanism to explain how oncogenic mutations regulate tumour microenvironment through cell-cell communication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ajuba family proteins link JNK to Hippo signaling.Sci Signal. 2013 Sep 10;6(292):ra81. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004324. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24023255 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of the Drosophila cell polarity regulator Scribbled promotes epithelial tissue overgrowth and cooperation with oncogenic Ras-Raf through impaired Hippo pathway signaling.BMC Dev Biol. 2011 Sep 29;11:57. doi: 10.1186/1471-213X-11-57. BMC Dev Biol. 2011. PMID: 21955824 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo pathway integrates PI3K-Akt signals with mechanical and polarity cues to control tissue growth.PLoS Biol. 2019 Oct 15;17(10):e3000509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000509. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31613895 Free PMC article.
-
A role for Hipk in the Hippo pathway.Sci Signal. 2013 May 14;6(275):pe18. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004259. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23674821 Review.
-
The Hippo size control pathway--ever expanding.Sci Signal. 2013 Jan 22;6(259):pe4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2003813. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 23354686 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory mechanism of FAT4 gene expression in response to actin dynamics during Src-induced carcinogenesis.PLoS One. 2015 Feb 13;10(2):e0118336. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118336. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25679223 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal cooperativity in heterogenous cancers.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Apr;64:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.08.028. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27582427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drosophila Models of Cell Polarity and Cell Competition in Tumourigenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1167:37-64. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-23629-8_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31520348 Review.
-
SRC tyrosine kinase activates the YAP/TAZ axis and thereby drives tumor growth and metastasis.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 15;294(7):2302-2317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004364. Epub 2018 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30559289 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory cellular hypertrophy: the other strategy for tissue homeostasis.Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;24(4):230-7. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Trends Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24239163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144: 646–674 - PubMed
-
- Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1996) Lessons from hereditary colorectal cancer. Cell 87: 159–170 - PubMed
-
- Frame MC (2002) Src in cancer: deregulation and consequences for cell behaviour. Biochim Biophys Acta 1602: 114–130 - PubMed
-
- Parsons SJ, Parsons JT (2004) Src family kinases, key regulators of signal transduction. Oncogene 23: 7906–7909 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

