Monomeric synucleins generate membrane curvature
- PMID: 23184946
- PMCID: PMC3548493
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.418871
Monomeric synucleins generate membrane curvature
Abstract
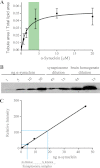
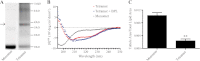
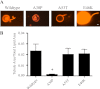
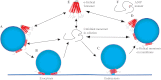
Synucleins are a family of presynaptic membrane binding proteins. α-Synuclein, the principal member of this family, is mutated in familial Parkinson disease. To gain insight into the molecular functions of synucleins, we performed an unbiased proteomic screen and identified synaptic protein changes in αβγ-synuclein knock-out brains. We observed increases in the levels of select membrane curvature sensing/generating proteins. One of the most prominent changes was for the N-BAR protein endophilin A1. Here we demonstrate that the levels of synucleins and endophilin A1 are reciprocally regulated and that they are functionally related. We show that all synucleins can robustly generate membrane curvature similar to endophilins. However, only monomeric but not tetrameric α-synuclein can bend membranes. Further, A30P α-synuclein, a Parkinson disease mutant that disrupts protein folding, is also deficient in this activity. This suggests that synucleins generate membrane curvature through the asymmetric insertion of their N-terminal amphipathic helix. Based on our findings, we propose to include synucleins in the class of amphipathic helix-containing proteins that sense and generate membrane curvature. These results advance our understanding of the physiological function of synucleins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
αβγ-Synuclein triple knockout mice reveal age-dependent neuronal dysfunction.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Nov 9;107(45):19573-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005005107. Epub 2010 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20974939 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Intrinsic Disorder in Human Synucleins and Associated Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8399. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158399. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125972 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular ageing of alpha- and Beta-synucleins: protein damage and repair mechanisms.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 22;8(4):e61442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061442. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23630590 Free PMC article.
-
The physiological role of α-synuclein and its relationship to Parkinson's Disease.J Neurochem. 2019 Sep;150(5):475-486. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14810. Epub 2019 Jul 28. J Neurochem. 2019. PMID: 31269263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synucleins and their relationship to Parkinson's disease.Cell Tissue Res. 2004 Oct;318(1):163-74. doi: 10.1007/s00441-004-0921-7. Epub 2004 Jul 24. Cell Tissue Res. 2004. PMID: 15503152 Review.
Cited by
-
α-Synuclein oligomers with broken helical conformation form lipoprotein nanoparticles.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 14;288(24):17620-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.476697. Epub 2013 Apr 22. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23609437 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein can inhibit SNARE-mediated vesicle fusion through direct interactions with lipid bilayers.Biochemistry. 2013 Apr 9;52(14):2385-7. doi: 10.1021/bi4002369. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23528131 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein Mutation Inhibits Endocytosis at Mammalian Central Nerve Terminals.J Neurosci. 2016 Apr 20;36(16):4408-14. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3627-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27098685 Free PMC article.
-
Parkinson's disease: proteinopathy or lipidopathy?NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2020 Jan 3;6:3. doi: 10.1038/s41531-019-0103-7. eCollection 2020. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2020. PMID: 31909184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hsp110 mitigates α-synuclein pathology in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Nov 26;116(48):24310-24316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1903268116. Epub 2019 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31685606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spillantini M. G., Schmidt M. L., Lee V. M., Trojanowski J. Q., Jakes R., Goedert M. (1997) α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388, 839–840 - PubMed
-
- Krüger R., Kuhn W., Müller T., Woitalla D., Graeber M., Kösel S., Przuntek H., Epplen J. T., Schöls L., Riess O. (1998) A30P mutation in the gene encoding α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 18, 106–108 - PubMed
-
- Polymeropoulos M. H., Lavedan C., Leroy E., Ide S. E., Dehejia A., Dutra A., Pike B., Root H., Rubenstein J., Boyer R., Stenroos E. S., Chandrasekharappa S., Athanassiadou A., Papapetropoulos T., Johnson W. G., Lazzarini A. M., Duvoisin R. C., Di Iorio G., Golbe L. I., Nussbaum R. L. (1997) Mutation in the α-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276, 2045–2047 - PubMed
-
- Zarranz J. J., Alegre J., Gómez-Esteban J. C., Lezcano E., Ros R., Ampuero I., Vidal L., Hoenicka J., Rodriguez O., Atarés B., Llorens V., Gomez Tortosa E., del Ser T., Muñoz D. G., de Yebenes J. G. (2004) The new mutation, E46K, of α-synuclein causes Parkinson and Lewy body dementia. Ann. Neurol. 55, 164–173 - PubMed
-
- Símon-Sánchez J., Schulte C., Bras J. M., Sharma M., Gibbs J. R., Berg D., Paisan-Ruiz C., Lichtner P., Scholz S. W., Hernandez D. G., Krüger R., Federoff M., Klein C., Goate A., Perlmutter J., Bonin M., Nalls M. A., Illig T., Gieger C., Houlden H., Steffens M., Okun M. S., Racette B. A., Cookson M. R., Foote K. D., Fernandez H. H., Traynor B. J., Schreiber S., Arepalli S., Zonozi R., Gwinn K., van der Brug M., Lopez G., Chanock S. J., Schatzkin A., Park Y., Hollenbeck A., Gao J., Huang X., Wood N. W., Lorenz D., Deuschl G., Chen H., Riess O., Hardy J. A., Singleton A. B., Gasser T. (2009) Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson's disease. Nat. Genet. 41, 1308–1312 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

