Identification of a potent combination of key Plasmodium falciparum merozoite antigens that elicit strain-transcending parasite-neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 23184525
- PMCID: PMC3553821
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01107-12
Identification of a potent combination of key Plasmodium falciparum merozoite antigens that elicit strain-transcending parasite-neutralizing antibodies
Abstract
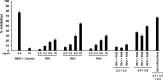
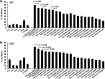
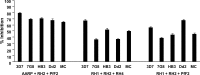
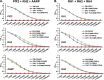
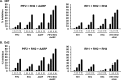
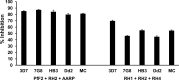
Blood-stage malaria vaccines that target single Plasmodium falciparum antigens involved in erythrocyte invasion have not induced optimal protection in field trials. Blood-stage malaria vaccine development has faced two major hurdles, antigenic polymorphisms and molecular redundancy, which have led to an inability to demonstrate potent, strain-transcending, invasion-inhibitory antibodies. Vaccines that target multiple invasion-related parasite proteins may inhibit erythrocyte invasion more efficiently. Our approach is to develop a receptor-blocking blood-stage vaccine against P. falciparum that targets the erythrocyte binding domains of multiple parasite adhesins, blocking their interaction with their receptors and thus inhibiting erythrocyte invasion. However, with numerous invasion ligands, the challenge is to identify combinations that elicit potent strain-transcending invasion inhibition. We evaluated the invasion-inhibitory activities of 20 different triple combinations of antibodies mixed in vitro against a diverse set of six key merozoite ligands, including the novel ligands P. falciparum apical asparagine-rich protein (PfAARP), EBA-175 (PfF2), P. falciparum reticulocyte binding-like homologous protein 1 (PfRH1), PfRH2, PfRH4, and Plasmodium thrombospondin apical merozoite protein (PTRAMP), which are localized in different apical organelles and are translocated to the merozoite surface at different time points during invasion. They bind erythrocytes with different specificities and are thus involved in distinct invasion pathways. The antibody combination of EBA-175 (PfF2), PfRH2, and PfAARP produced the most efficacious strain-transcending inhibition of erythrocyte invasion against diverse P. falciparum clones. This potent antigen combination was selected for coimmunization as a mixture that induced balanced antibody responses against each antigen and inhibited erythrocyte invasion efficiently. We have thus demonstrated a novel two-step screening approach to identify a potent antigen combination that elicits strong strain-transcending invasion inhibition, supporting its development as a receptor-blocking malaria vaccine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bacterially expressed full-length recombinant Plasmodium falciparum RH5 protein binds erythrocytes and elicits potent strain-transcending parasite-neutralizing antibodies.Infect Immun. 2014 Jan;82(1):152-64. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00970-13. Epub 2013 Oct 14. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24126527 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing blockade of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte invasion: assessing combinations of antibodies against PfRH5 and other merozoite antigens.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(11):e1002991. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002991. Epub 2012 Nov 8. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 23144611 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-Dependent Inhibition of Erythrocyte Invasion by Monoclonal Antibodies Against Plasmodium falciparum CyRPA.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 10;12:716305. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.716305. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34447381 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between anti-merozoite antibodies and incidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS Med. 2010 Jan 19;7(1):e1000218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000218. PLoS Med. 2010. PMID: 20098724 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of naturally acquired immunity to P. falciparum and approaches to identify merozoite antigen targets.Parasitology. 2018 Jun;145(7):839-847. doi: 10.1017/S0031182017001949. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Parasitology. 2018. PMID: 29144217 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmodium falciparum Cysteine-Rich Protective Antigen (CyRPA) Elicits Detectable Levels of Invasion-Inhibitory Antibodies during Natural Infection in Humans.Infect Immun. 2022 Jan 25;90(1):e0037721. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00377-21. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Infect Immun. 2022. PMID: 34694918 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of parasite invasion by monoclonal antibody against epidermal growth factor-like domain of Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 1 paralog.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 7;9(1):3906. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40321-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30846737 Free PMC article.
-
Strain-transcending neutralization of malaria parasite by antibodies against Plasmodium falciparum enolase.Malar J. 2018 Aug 20;17(1):304. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2455-6. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 30126436 Free PMC article.
-
Antibodies against a short region of PfRipr inhibit Plasmodium falciparum merozoite invasion and PfRipr interaction with Rh5 and SEMA7A.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 20;10(1):6573. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63611-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32313230 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination with conserved regions of erythrocyte-binding antigens induces neutralizing antibodies against multiple strains of Plasmodium falciparum.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 10;8(9):e72504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072504. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24039774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray CJ, Rosenfeld LC, Lim SS, Andrews KG, Foreman KJ, Haring D, Fullman N, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Lopez AD. 2012. Global malaria mortality between 1980 and 2010: a systematic analysis. Lancet 379:413–431 - PubMed
-
- Ogutu BR, Apollo OJ, McKinney D, Okoth W, Siangla J, Dubovsky F, Tucker K, Waitumbi JN, Diggs C, Watts J, Malkin E, Leach A, Soisson LA, Milman JB, Otieno L, Holland CA, Polhemus M, Remich SA, Ockenhouse CF, Cohen J, Ballou WR, Martin SK, Angov E, Stewart VA, Lyon JA, Heppner DG, Withers MR. 2009. Blood stage malaria vaccine eliciting high antigen-specific antibody concentrations confers no protection to young children in Western Kenya. PLoS One 4:e4708 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004708 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Spring MD, Cummings JF, Ockenhouse CF, Dutta S, Reidler R, Angov E, Bergmann-Leitner E, Stewart VA, Bittner S, Juompan L, Kortepeter MG, Nielsen R, Krzych U, Tierney E, Ware LA, Dowler M, Hermsen CC, Sauerwein RW, DE Vlas SJ, Ofori-Anyinam O, Lanar DE, Williams JL, Kester KE, Tucker K, Shi M, Malkin E, Long C, Diggs CL, Soisson L, Dubois MC, Ballou WR, Cohen J, Heppner DG., Jr 2009. Phase 1/2a study of the malaria vaccine candidate apical membrane antigen-1 (AMA-1) administered in adjuvant system AS01B or AS02A. PLoS One 4:e5254 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005254 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thera MA, Doumbo OK, Coulibaly D, Laurens MB, Ouattara A, Kone AK, Guindo AB, Traore K, Traore I, Kouriba B, Diallo DA, Diarra I, Daou M, Dolo A, Tolo Y, Sissoko MS, Niangaly A, Sissoko M, Takala-Harrison S, Lyke KE, Wu Y, Blackwelder WC, Godeaux O, Vekemans J, Dubois MC, Ballou WR, Cohen J, Thompson D, Dube T, Soisson L, Diggs CL, House B, Lanar DE, Dutta S, Heppner DG, Jr, Plowe CV. 2011. A field trial to assess a blood-stage malaria vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 365:1004–1013 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

