Structural insight into inhibitor of apoptosis proteins recognition by a potent divalent smac-mimetic
- PMID: 23166698
- PMCID: PMC3499469
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049527
Structural insight into inhibitor of apoptosis proteins recognition by a potent divalent smac-mimetic
Abstract
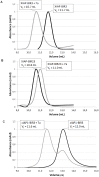
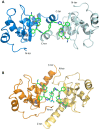
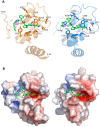
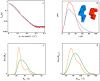
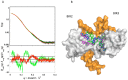
Genetic alterations enhancing cell survival and suppressing apoptosis are hallmarks of cancer that significantly reduce the efficacy of chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein (IAP) family hosts conserved proteins in the apoptotic pathway whose over-expression, frequently found in tumours, potentiates survival and resistance to anticancer agents. In humans, IAPs comprise eight members hosting one or more structural Baculoviral IAP Repeat (BIR) domains. Cellular IAPs (cIAP1 and 2) indirectly inhibit caspase-8 activation, and regulate both the canonical and the non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathways. In contrast to cIAPs, XIAP (X chromosome-linked Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein) inhibits directly the effector caspases-3 and -7 through its BIR2 domain, and initiator caspase-9 through its BIR3 domain; molecular docking studies suggested that Smac/DIABLO antagonizes XIAP by simultaneously targeting both BIR2 and BIR3 domains. Here we report analytical gel filtration, crystallographic and SAXS experiments on cIAP1-BIR3, XIAP-BIR3 and XIAP-BIR2BIR3 domains, alone and in the presence of compound 9a, a divalent homodimeric Smac mimetic. 9a is shown to bind two BIR domains inter- (in the case of two BIR3) and intra-molecularly (in the case of XIAP-BIR2BIR3), with higher affinity for cIAP1-BIR3, relative to XIAP-BIR3. Despite the different crystal lattice packing, 9a maintains a right handed helical conformation in both cIAP1-BIR3 and XIAP-BIR3 crystals, that is likely conserved in solution as shown by SAXS data. Our structural results demonstrate that the 9a linker length, its conformational degrees of freedom and its hydrophobicity, warrant an overall compact structure with optimal solvent exposure of its two active moieties for IAPs binding. Our results show that 9a is a good candidate for pre-clinical and clinical studies, worth of further investigations in the field of cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural basis for bivalent Smac-mimetics recognition in the IAP protein family.J Mol Biol. 2009 Sep 25;392(3):630-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.033. Epub 2009 Apr 22. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19393243
-
Structure-based design and molecular profiling of Smac-mimetics selective for cellular IAPs.FEBS J. 2018 Sep;285(17):3286-3298. doi: 10.1111/febs.14616. Epub 2018 Aug 16. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 30055105
-
Characterization of Potent SMAC Mimetics that Sensitize Cancer Cells to TNF Family-Induced Apoptosis.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 12;11(9):e0161952. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161952. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27617834 Free PMC article.
-
Bivalent SMAC Mimetics for Treating Cancer by Antagonizing Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins.ChemMedChem. 2019 Dec 4;14(23):1951-1962. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.201900410. Epub 2019 Nov 19. ChemMedChem. 2019. PMID: 31692274 Review.
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein - a critical death resistance regulator and therapeutic target for personalized cancer therapy.Front Oncol. 2014 Jul 28;4:197. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00197. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25120954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Smac mimetics induce inflammation and necrotic tumour cell death by modulating macrophage activity.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Nov 14;4(11):e920. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.449. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 24232096 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-based identification of a new IAP-targeting compound that induces cancer cell death inducing NF-κB pathway.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Nov 26;19:6366-6374. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.11.034. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34938412 Free PMC article.
-
The Photoperiod Regulates Granulosa Cell Apoptosis through the FSH-Nodal/ALK7 Signaling Pathway in Phodopus sungorus.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;12(24):3570. doi: 10.3390/ani12243570. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36552491 Free PMC article.
-
The TwistDock workflow for evaluation of bivalent Smac mimetics targeting XIAP.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Apr 26;13:1373-1388. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S194276. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31118573 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy Testing in a Spheroid-based 3D Cell Culture Model for Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Vis Exp. 2018 Apr 20;(134):57012. doi: 10.3791/57012. J Vis Exp. 2018. PMID: 29733308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Steller H (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267: 1445–1449. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins–suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13: 239–252. - PubMed
-
- LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG, MacKenzie AE (1998) The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging role in cancer. Oncogene 17: 3247–3259. - PubMed
-
- Kulathila R, Vash B, Sage D, Cornell-Kennon S, Wright K, et al. (2009) The structure of the BIR3 domain of cIAP1 in complex with the N-terminal peptides of SMAC and caspase-9. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 65: 58–66. - PubMed
-
- Wu G, Chai J, Suber TL, Wu JW, Du C, et al. (2000) Structural basis of IAP recognition by Smac/DIABLO. Nature 408: 1008–1012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

