G protein trafficking
- PMID: 23161140
- PMCID: PMC5936075
- DOI: 10.1007/978-94-007-4765-4_11
G protein trafficking
Abstract
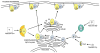
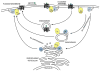
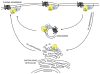
The classical view of heterotrimeric G protein signaling places G -proteins at the cytoplasmic surface of the cell's plasma membrane where they are activated by an appropriate G protein-coupled receptor. Once activated, the GTP-bound Gα and the free Gβγ are able to regulate plasma membrane-localized effectors, such as adenylyl cyclase, phospholipase C-β, RhoGEFs and ion channels. Hydrolysis of GTP by the Gα subunit returns the G protein to the inactive Gαβγ heterotrimer. Although all of these events in the G protein cycle can be restricted to the cytoplasmic surface of the plasma membrane, G protein localization is dynamic. Thus, it has become increasingly clear that G proteins are able to move to diverse subcellular locations where they perform non-canonical signaling functions. This chapter will highlight our current understanding of trafficking pathways that target newly synthesized G proteins to the plasma membrane, activation-induced and reversible translocation of G proteins from the plasma membrane to intracellular locations, and constitutive trafficking of G proteins.
Figures
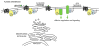
Similar articles
-
G protein-regulated endocytic trafficking of adenylyl cyclase type 9.Elife. 2020 Jun 9;9:e58039. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58039. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32515353 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical signaling and localizations of heterotrimeric G proteins.Cell Signal. 2012 Jan;24(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.08.014. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 21907280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seven transmembrane receptor core signaling complexes are assembled prior to plasma membrane trafficking.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 10;281(45):34561-73. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M605012200. Epub 2006 Sep 7. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16959776
-
Regulation of post-Golgi traffic of G protein-coupled receptors.Subcell Biochem. 2012;63:83-95. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4765-4_5. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23161134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Introduction: G Protein-coupled Receptors and RGS Proteins.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;133:1-11. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.03.002. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26123299 Review.
Cited by
-
Visualization of endogenous G proteins on endosomes and other organelles.Elife. 2024 Nov 8;13:RP97033. doi: 10.7554/eLife.97033. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39514269 Free PMC article.
-
A dynamic partitioning mechanism polarizes membrane protein distribution.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 30;14(1):7909. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43615-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38036511 Free PMC article.
-
Stearic acid blunts growth-factor signaling via oleoylation of GNAI proteins.Nat Commun. 2021 Jul 28;12(1):4590. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24844-9. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34321466 Free PMC article.
-
A short C-terminal peptide in Gγ regulates Gβγ signaling efficacy.Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Aug 1;32(16):1446-1458. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E20-11-0750. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34106735 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Molecule, Super-Resolution, and Functional Analysis of G Protein-Coupled Receptor Behavior Within the T Cell Immunological Synapse.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 18;8:608484. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.608484. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33537301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akgoz M, Kalyanaraman V, Gautam N. Receptor-mediated reversible translocation of the G protein betagamma complex from the plasma membrane to the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(49):51541–51544. - PubMed
-
- Allen JA, Yu JZ, Donati RJ, Rasenick MM. Beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation promotes G alpha s internalization through lipid rafts: a study in living cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;67(5):1493–1504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

