Acinetobacter baumannii rOmpA vaccine dose alters immune polarization and immunodominant epitopes
- PMID: 23153442
- PMCID: PMC3557524
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.11.008
Acinetobacter baumannii rOmpA vaccine dose alters immune polarization and immunodominant epitopes
Abstract
Background: The rOmpA vaccine has been shown to protect mice from lethal infection caused by extreme-drug-resistant (XDR) Acinetobacter baumannii. The role of dose in immunology of the rOmpA vaccine was explored.
Methods: Mice were vaccinated with various doses of rOmpA plus aluminum hydroxide (Al(OH)(3)) adjuvant. The impact of dose on antibody titers, cytokine production, and immunodominant epitopes was defined.
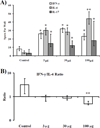
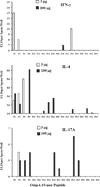
Results: Anti-rOmpA IgG and IgG subtype titers were higher at larger vaccine doses (30 and 100 μg vs. 3 μg). The 3 μg dose induced a balanced IFN-γ-IL-4 immune response while the 100 μg dose induced a polarized IL-4/Type 2 response. Epitope mapping revealed distinct T cell epitopes that activated IFN-γ-, IL-4-, and IL-17-producing splenocytes. Vaccination with the 100 μg dose caused epitope spreading among IL-4-producing splenocytes, while it induced fewer reactive epitopes among IFN-γ-producing splenocytes.
Conclusions: Vaccine dose escalation resulted in an enhanced Type 2 immune response, accompanied by substantial IL-4-inducing T cell epitope spreading and restricted IFN-γ-inducing epitopes. These results inform continued development of the rOmpA vaccine against A. baumannii, and also are of general importance in that they indicate that immune polarization and epitope selectivity can be modulated by altering vaccine dose.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
LL and BS have filed a patent for the rOmpA vaccine.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Active and passive immunization protects against lethal, extreme drug resistant-Acinetobacter baumannii infection.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029446. Epub 2012 Jan 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253723 Free PMC article.
-
A Multiepitope Peptide, rOmp22, Encapsulated in Chitosan-PLGA Nanoparticles as a Candidate Vaccine Against Acinetobacter baumannii Infection.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 4;16:1819-1836. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S296527. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33707942 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoprotective potential of in silico predicted Acinetobacter baumannii outer membrane nuclease, NucAb.Int J Med Microbiol. 2016 Jan;306(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Nov 12. Int J Med Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26614015
-
Identification and selection of immunodominant B and T cell epitopes for dengue multi-epitope-based vaccine.Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021 Feb;210(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s00430-021-00700-x. Epub 2021 Jan 30. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33515283 Review.
-
Mucosal immunization with purified OmpA elicited protective immunity against infections caused by multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.Microb Pathog. 2016 Jul;96:20-5. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2016.04.019. Epub 2016 Apr 29. Microb Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27133268 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel mRNA multi-epitope vaccine of Acinetobacter baumannii based on multi-target protein design in immunoinformatic approach.BMC Genomics. 2024 Aug 19;25(1):791. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10691-7. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39160492 Free PMC article.
-
Acinetobacter baumannii Infection and IL-17 Mediated Immunity.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:9834020. doi: 10.1155/2016/9834020. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 26977122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloning of ompA gene from Acinetobacter baumannii into the eukaryotic expression vector pBudCE4.1 as DNA vaccine.Indian J Microbiol. 2018 Jun;58(2):174-181. doi: 10.1007/s12088-017-0705-x. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Indian J Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29651176 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosphingolipids (GSLs) from Sphingomonas paucimobilis Increase the Efficacy of Liposome-Based Nanovaccine against Acinetobacter baumannii-Associated Pneumonia in Immunocompetent and Immunocompromised Mice.Molecules. 2022 Nov 12;27(22):7790. doi: 10.3390/molecules27227790. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36431892 Free PMC article.
-
The Hyr1 protein from the fungus Candida albicans is a cross kingdom immunotherapeutic target for Acinetobacter bacterial infection.PLoS Pathog. 2018 May 10;14(5):e1007056. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007056. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29746596 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Higgins PG, Dammhayn C, Hackel M, Seifert H. Global spread of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010 Feb;65(2):233–238. - PubMed
-
- Rosenthal VD, Maki DG, Jamulitrat S, Medeiros EA, Todi SK, Gomez DY, et al. International Nosocomial Infection Control Consortium (INICC) report, data summary for 2003–2008, issued June 2009. American journal of infection control. 2010 Mar;38(2):95–104 e2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

