IL-4 and IFN-γ induced by human immunodeficiency virus vaccine in a schistosome infection model
- PMID: 23151453
- PMCID: PMC3601131
- DOI: 10.4161/hv.22142
IL-4 and IFN-γ induced by human immunodeficiency virus vaccine in a schistosome infection model
Abstract
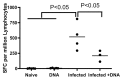
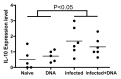
The co-infection of HIV and helminth parasites, such as Schistosoma spp, has increased in sub-Saharan Africa. Many HIV vaccine candidate studies have been completed or are in ongoing clinical trials, but it is not clear how HIV vaccines might affect the course of schistosome infections. In this study, we immunized S. mansoni-infected mice with an efficient DNA vaccine that included HIV gag. Using this model, we found that Th2 cytokines, such as IL-4 and IL-13, were highly induced after schistosome infection. Treatment of infected mice with the HIV DNA vaccine resulted in a significant attenuation of this rise in IL-13 expression and an increase in expression of the Th1 cytokine, TNF-α. However, vaccine administration did not significantly influence the expression of IL-4, or IFN-γ, and did not affect T cell proliferative capacity. Interestingly, the IL-4 (+) IFN-γ (+) phenotype appears in schistosome-infected mice that received HIV vaccination, and is associated with the expression of transcription factors GATA3 (+) T-bet (+) in these mice. These studies indicate that DNA vaccination can have an impact on ongoing chronic infection.
Keywords: HIV vaccine; Th1 and Th2 responses; schistosome infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 vaccine-specific responses induced by Listeria vector vaccines are maintained in mice subsequently infected with a model helminth parasite, Schistosoma mansoni.Vaccine. 2013 Nov 19;31(48):5651-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.09.067. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 24120546
-
Downregulation of Th1 cytokine production accompanies induction of Th2 responses by a parasitic helminth, Schistosoma mansoni.J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):159-66. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.159. J Exp Med. 1991. PMID: 1824635 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of helminth infection restores HIV-1C vaccine-specific T cell responses independent of helminth-induced IL-10.Vaccine. 2010 Feb 3;28(5):1310-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.11.019. Epub 2009 Nov 24. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 19941988 Free PMC article.
-
Helminth infection suppresses T-cell immune response to HIV-DNA-based vaccine in mice.Vaccine. 2006 Jun 12;24(24):5211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2006.03.078. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Vaccine. 2006. PMID: 16675073
-
Development of an antipathology vaccine for schistosomiasis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996 Oct 25;797:191-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1996.tb52960.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1996. PMID: 8993362 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic schistosomiasis suppresses HIV-specific responses to DNA-MVA and MVA-gp140 Env vaccine regimens despite antihelminthic treatment and increases helminth-associated pathology in a mouse model.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jul 26;14(7):e1007182. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007182. eCollection 2018 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30048550 Free PMC article.
-
IL-4 suppresses the responses to TLR7 and TLR9 stimulation and increases the permissiveness to retroviral infection of murine conventional dendritic cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 29;9(1):e87668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087668. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24489947 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
