Characterization of a distinct population of circulating human non-adherent endothelial forming cells and their recruitment via intercellular adhesion molecule-3
- PMID: 23144795
- PMCID: PMC3492591
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046996
Characterization of a distinct population of circulating human non-adherent endothelial forming cells and their recruitment via intercellular adhesion molecule-3
Abstract
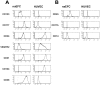
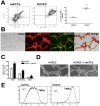
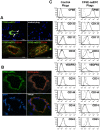
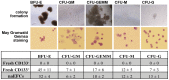
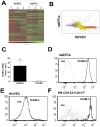
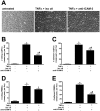
Circulating vascular progenitor cells contribute to the pathological vasculogenesis of cancer whilst on the other hand offer much promise in therapeutic revascularization in post-occlusion intervention in cardiovascular disease. However, their characterization has been hampered by the many variables to produce them as well as their described phenotypic and functional heterogeneity. Herein we have isolated, enriched for and then characterized a human umbilical cord blood derived CD133(+) population of non-adherent endothelial forming cells (naEFCs) which expressed the hematopoietic progenitor cell markers (CD133, CD34, CD117, CD90 and CD38) together with mature endothelial cell markers (VEGFR2, CD144 and CD31). These cells also expressed low levels of CD45 but did not express the lymphoid markers (CD3, CD4, CD8) or myeloid markers (CD11b and CD14) which distinguishes them from 'early' endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs). Functional studies demonstrated that these naEFCs (i) bound Ulex europaeus lectin, (ii) demonstrated acetylated-low density lipoprotein uptake, (iii) increased vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1) surface expression in response to tumor necrosis factor and (iv) in co-culture with mature endothelial cells increased the number of tubes, tubule branching and loops in a 3-dimensional in vitro matrix. More importantly, naEFCs placed in vivo generated new lumen containing vasculature lined by CD144 expressing human endothelial cells (ECs). Extensive genomic and proteomic analyses of the naEFCs showed that intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-3 is expressed on their cell surface but not on mature endothelial cells. Furthermore, functional analysis demonstrated that ICAM-3 mediated the rolling and adhesive events of the naEFCs under shear stress. We suggest that the distinct population of naEFCs identified and characterized here represents a new valuable therapeutic target to control aberrant vasculogenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human cord blood-derived AC133+ progenitor cells preserve endothelial progenitor characteristics after long term in vitro expansion.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 11;5(2):e9173. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009173. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20161785 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial cells from cord blood CD133+CD34+ progenitors share phenotypic, functional and gene expression profile similarities with lymphatics.J Cell Mol Med. 2009 Mar;13(3):522-34. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00340.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 18410526 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial progenitor cell culture and differentiation in vitro: a methodological comparison using human umbilical cord blood.Cardiovasc Res. 2003 May 1;58(2):478-86. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(03)00252-9. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. PMID: 12757882
-
Endothelial progenitor cells in angiogenesis.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2005 Feb 25;57(1):1-6. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 15719128 Review.
-
Endothelial heterogeneity and their relevance in cardiac development and coronary artery disease.Vascul Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;153:107242. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107242. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Vascul Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37940065 Review.
Cited by
-
EphA1 activation promotes the homing of endothelial progenitor cells to hepatocellular carcinoma for tumor neovascularization through the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Apr 11;35:65. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0339-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27066828 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate is a ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ that regulates neoangiogenesis.FASEB J. 2015 Sep;29(9):3638-53. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-261289. Epub 2015 May 18. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25985799 Free PMC article.
-
An Essential NRP1-Mediated Role for Tagln2 in Gastric Cancer Angiogenesis.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 4;11:653246. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.653246. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34150622 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted cell delivery of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for cardiovascular disease applications: a review of preclinical advancements.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 4;10:1236345. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1236345. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37600026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Don't go in circles: confounding factors in gene expression profiling.EMBO J. 2018 Jun 1;37(11):e97945. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797945. Epub 2018 May 7. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 29735571 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho HJ, Kim HS, Lee MM, Kim DH, Yang HJ, et al. (2003) Mobilized endothelial progenitor cells by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor accelerate reendothelialization and reduce vascular inflammation after intravascular radiation. Circulation 108: 2918–2925. - PubMed
-
- Laing AJ, Dillon JP, Condon ET, Street JT, Wang JH, et al. (2007) Mobilization of endothelial precursor cells: systemic vascular response to musculoskeletal trauma. J Orthop Res 25: 44–50. - PubMed
-
- Kawamoto A, Gwon HC, Iwaguro H, Yamaguchi JI, Uchida S, et al. (2001) Therapeutic potential of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for myocardial ischemia. Circulation 103: 634–637. - PubMed
-
- Kocher AA, Schuster MD, Szabolcs MJ, Takuma S, Burkhoff D, et al. (2001) Neovascularization of ischemic myocardium by human bone-marrow-derived angioblasts prevents cardiomyocyte apoptosis, reduces remodeling and improves cardiac function. Nat Med 7: 430–436. - PubMed
-
- Lyden D, Hattori K, Dias S, Costa C, Blaikie P, et al. (2001) Impaired recruitment of bone-marrow-derived endothelial and hematopoietic precursor cells blocks tumor angiogenesis and growth. Nat Med 7: 1194–1201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

