Prognostic significance of membrane-associated mucins 1 and 4 in gastric adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 23139719
- PMCID: PMC3460289
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2012.598
Prognostic significance of membrane-associated mucins 1 and 4 in gastric adenocarcinoma
Abstract
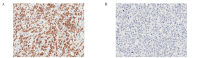
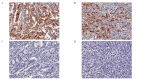
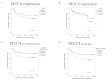
Aberrant expression of mucins is likely associated with cancer biology as alterations in the expression and/or glycosylation patterns of various mucins have been noted. Expression of the mucin family in gastric cancers has been reported in numerous studies, but the results are conflicting. Therefore, we investigated the potential use of mucin (MUC)1 and 4 as prognostic markers in gastric cancer according to histological subtype. Three-hundred and sixty-five gastric adenocarcinoma patients who underwent surgical resection were selected for this study. Among the 365 gastric cancer samples tested here, 34% consisted of early gastric cancer and 66% were advanced. In terms of location, 68.7% of the cohort had intestinal-type cancer and 30.7% had diffuse-type. We constructed tissue microarrays with formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded blocks of gastric cancer and these micro-arrays were evaluated for phenotypic expression of MUC1/4 using monoclonal antibodies. Two-hundred and ninety-two patients (92.7%) were positive for MUC1 and 216 (60.5%) were positive for MUC4. MUC1 expression was not correlated with any other clinicopathological variables such as age, gender, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis, Lauren classification or recurrence. However, loss of MUC4 expression was significantly correlated with recurrence (p=0.033). MUC4 expression was also significantly correlated with better disease-free survival (p=0.049) and particularly in the intestinal-type (p=0.018). Our present findings demonstrated that loss of MUC4 expression can be used as a prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Loss of MUC4 expression is a prognostic indicator of increased recurrence and poor disease-free survival in patients with gastric cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MUC4 and MUC1 expression in adenocarcinoma of the stomach correlates with vessel invasion and lymph node metastasis: an immunohistochemical study of early gastric cancer.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049251. Epub 2012 Nov 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23152882 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of mucins and E-cadherin in gastric carcinoma and their clinical significance.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Oct 15;10(20):3044-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i20.3044. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15378790 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical impact of MUC1 and MUC4 expression in Barrett-associated oesophageal adenocarcinoma.J Clin Pathol. 2009 Dec;62(12):1144-6. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2008.060780. J Clin Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19946103
-
Expression of mucin antigens in human cancers and its relationship with malignancy potential.Pathol Int. 1997 Dec;47(12):813-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1997.tb03713.x. Pathol Int. 1997. PMID: 9503463 Review.
-
Mucins in neoplasms of pancreas, ampulla of Vater and biliary system.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016 Oct 15;8(10):725-734. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v8.i10.725. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27795812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Mucin Expression in the Diagnosis of Oesophago-Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 1;15(21):5252. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215252. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of progressive metaplasia in the gastric corpus mucosa of Mongolian gerbils infected with Helicobacter pylori.J Pathol. 2016 Aug;239(4):399-410. doi: 10.1002/path.4735. Epub 2016 Jun 22. J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27125972 Free PMC article.
-
Mucin-microbiome signatures shape the tumor microenvironment in gastric cancer.Microbiome. 2023 Apr 21;11(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01534-w. Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 37085819 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and prognostic significance of MUC1 expression in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after radical resection.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2018 May-Jun;24(3):165-170. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_420_17. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 29798942 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and bioinformatics analysis of overlapping differentially expressed genes in depression, papillary thyroid cancer and uterine fibroids.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Jun;15(6):4810-4816. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6023. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29805500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li XH, Zheng HC, Wang ZG, et al. The clinicopathological and prognostic significance of MUC-1 expression in Japanese gastric carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study of tissue micro-arrays. Anticancer Res. 2008;28:1061–1067. - PubMed
-
- Hollingsworth MA, Swanson BJ. Mucins in cancer: protection and control of the cell surface. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:45–60. - PubMed
-
- Zheng H, Takahashi H, Nakajima T, et al. MUC6 down-regulation correlates with gastric carcinoma progression and a poor prognosis: an immunohistochemical study with tissue micro-arrays. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006;132:817–823. - PubMed
-
- Cozzi PJ, Wang J, Delprado W, et al. MUC1, MUC2, MUC4, MUC5AC and MUC6 expression in the progression of prostate cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2005;22:565–573. - PubMed
-
- Fattorossi A, Battaglia A, Malinconico P, et al. Constitutive and inducible expression of the epithelial antigen MUC1 (CD227) in human T cells. Exp Cell Res. 2002;280:107–118. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
