Presenilin-1 adopts pathogenic conformation in normal aging and in sporadic Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 23138650
- PMCID: PMC3552123
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-012-1065-6
Presenilin-1 adopts pathogenic conformation in normal aging and in sporadic Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
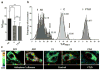
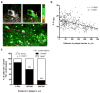
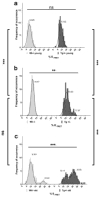
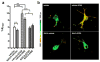
Accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, inflammation and synaptic and neuronal loss are some of the major neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD). While genetic mutations in amyloid precursor protein and presenilin-1 and -2 (PS1 and PS2) genes cause early-onset familial AD, the etiology of sporadic AD is not fully understood. Our current study shows that changes in conformation of endogenous wild-type PS1, similar to those found with mutant PS1, occur in sporadic AD brain and during normal aging. Using a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (Tg2576) that overexpresses the Swedish mutation of amyloid precursor protein but has normal levels of endogenous wild-type presenilin, we report that the percentage of PS1 in a pathogenic conformation increases with age. Importantly, we found that this PS1 conformational shift is associated with amyloid pathology and precedes amyloid-β deposition in the brain. Furthermore, we found that oxidative stress, a common stress characteristic of aging and AD, causes pathogenic PS1 conformational change in neurons in vitro, which is accompanied by increased Aβ42/40 ratio. The results of this study provide important information about the timeline of pathogenic changes in PS1 conformation during aging and suggest that structural changes in PS1/γ-secretase may represent a molecular mechanism by which oxidative stress triggers amyloid-β accumulation in aging and in sporadic AD brain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A presenilin-1 mutation identified in familial Alzheimer disease with cotton wool plaques causes a nearly complete loss of gamma-secretase activity.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 16;285(29):22350-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.116962. Epub 2010 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20460383 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic presenilin 1 and synaptotagmin 1 interaction modulates exocytosis and amyloid β production.Mol Neurodegener. 2017 Feb 13;12(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0159-y. Mol Neurodegener. 2017. PMID: 28193235 Free PMC article.
-
Presenilin 1 regulates the processing of beta-amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments and the generation of amyloid beta-protein in endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi.Biochemistry. 1998 Nov 24;37(47):16465-71. doi: 10.1021/bi9816195. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9843412
-
Genes and mechanisms involved in beta-amyloid generation and Alzheimer's disease.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999;249(6):266-70. doi: 10.1007/s004060050098. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10653281 Review.
-
Dynamic Nature of presenilin1/γ-Secretase: Implication for Alzheimer's Disease Pathogenesis.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Mar;55(3):2275-2284. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0487-5. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28332150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation are upstream of amyloid pathology.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Dec;84:109-19. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26102023 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating Effect of Diet on Alzheimer's Disease.Diseases. 2019 Jan 26;7(1):12. doi: 10.3390/diseases7010012. Diseases. 2019. PMID: 30691140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin and Resveratrol in the Management of Cognitive Disorders: What is the Clinical Evidence?Molecules. 2016 Sep 17;21(9):1243. doi: 10.3390/molecules21091243. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27649135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic PS1 phosphorylation at Ser367.Elife. 2017 Jan 30;6:e19720. doi: 10.7554/eLife.19720. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28132667 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Polysaccharides in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 4;14:917629. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.917629. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35860666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Annaert WG, Esselens C, Baert V, et al. Interaction with telencephalin and the amyloid precursor protein predicts a ring structure for presenilins. Neuron. 2001;32(4):579–589. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada PV, Marzloff K, Hyman BT. Distribution of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in nondemented elderly individuals matches the pattern in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1992;42(9):1681–1688. - PubMed
-
- Berezovska O, Frosch M, McLean P, et al. The Alzheimer-related gene presenilin 1 facilitates notch 1 in primary mammalian neurons. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1999;69(2):273–280. - PubMed
-
- Borchelt DR, Thinakaran G, Eckman CB, et al. Familial Alzheimer’s disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Abeta1–42/1–40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron. 1996;17(5):1005–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

