Fibroblast cluster formation on 3D collagen matrices requires cell contraction dependent fibronectin matrix organization
- PMID: 23117111
- PMCID: PMC3563764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.10.005
Fibroblast cluster formation on 3D collagen matrices requires cell contraction dependent fibronectin matrix organization
Abstract
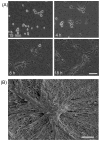
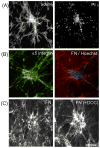
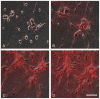
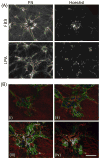
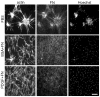
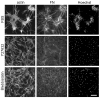
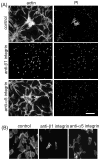
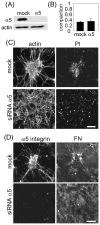
Fibroblasts incubated on 3D collagen matrices in serum or lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-containing medium self-organize into clusters through a mechanism that requires cell contraction. However, in platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-containing medium, cells migrate as individuals and do not form clusters even though they constantly encounter each other. Here, we present evidence that a required function of cell contraction in clustering is formation of fibronectin (FN) fibrillar matrix. We found that in serum or LPA but not in PDGF or basal medium, cells organized FN (both serum and cellular) into a fibrillar, detergent-insoluble matrix. Cell clusters developed concomitant with FN matrix formation. FN fibrils accumulated beneath cells and along the borders of cell clusters in regions of cell-matrix tension. Blocking Rho kinase or myosin II activity prevented FN matrix assembly and cell clustering. Using siRNA silencing and function-blocking antibodies and peptides, we found that cell clustering and FN matrix assembly required α5β1 integrins and fibronectin. Cells were still able to exert contractile force and compact the collagen matrix under the latter conditions, which showed that contraction was not sufficient for cell clustering to occur. Our findings provide new insights into how procontractile (serum/LPA) and promigratory (PDGF) growth factor environments can differentially regulate FN matrix assembly by fibroblasts interacting with collagen matrices and thereby influence mesenchymal cell morphogenetic behavior under physiologic circumstances such as wound repair, morphogenesis and malignancy.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibroblast morphogenesis on 3D collagen matrices: the balance between cell clustering and cell migration.Exp Cell Res. 2013 Oct 1;319(16):2440-6. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 May 9. Exp Cell Res. 2013. PMID: 23664837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Thrombin and Cell Contractility in Regulating Clustering and Collective Migration of Corneal Fibroblasts in Different ECM Environments.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015 Mar 3;56(3):2079-90. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16388. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25736789 Free PMC article.
-
PDGF‑stimulated dispersal of cell clusters and disruption of fibronectin matrix on three-dimensional collagen matrices requires matrix metalloproteinase-2.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Mar 15;26(6):1098-105. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-09-1396. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25589674 Free PMC article.
-
Full-Length Fibronectin Drives Fibroblast Accumulation at the Surface of Collagen Microtissues during Cell-Induced Tissue Morphogenesis.PLoS One. 2016 Aug 26;11(8):e0160369. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0160369. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27564551 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblasts in three dimensional matrices: cell migration and matrix remodeling.Exp Mol Med. 2009 Dec 31;41(12):858-65. doi: 10.3858/emm.2009.41.12.096. Exp Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19745603 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Collaboration of fibronectin matrix with other extracellular signals in morphogenesis and differentiation.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016 Oct;42:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2016.03.014. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27062478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast-fibronectin patterning and network formation in 3D fibrin matrices.Matrix Biol. 2017 Dec;64:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Matrix Biol. 2017. PMID: 28602859 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of opticin on bioactivity of retinal vascular endothelial cells cultured in collagen.Int J Ophthalmol. 2020 Aug 18;13(8):1202-1209. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2020.08.05. eCollection 2020. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32821673 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular disease-causing mutation, smooth muscle α-actin R258C, dominantly suppresses functions of α-actin in human patient fibroblasts.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jul 11;114(28):E5569-E5578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1703506114. Epub 2017 Jun 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28652363 Free PMC article.
-
Release of tensile strain on engineered human tendon tissue disturbs cell adhesions, changes matrix architecture, and induces an inflammatory phenotype.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 21;9(1):e86078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086078. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24465881 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

