ER stress activates NF-κB by integrating functions of basal IKK activity, IRE1 and PERK
- PMID: 23110043
- PMCID: PMC3482226
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045078
ER stress activates NF-κB by integrating functions of basal IKK activity, IRE1 and PERK
Abstract
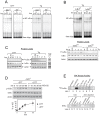
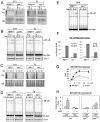
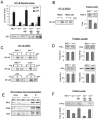
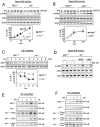
NF-κB, a transcription factor, becomes activated during the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR), an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response pathway. NF-κB is normally held inactive by its inhibitor, IκBα. Multiple cellular pathways activate IKK (IκBα Kinase) which phosphorylate IκBα leading to its degradation and NF-κB activation. Here, we find that IKK is required for maximum activation of NF-κB in response to ER stress. However, unlike canonical NFκB activation, IKK activity does not increase during ER stress, but rather the level of basal IKK activity is critical for determining the extent of NF-κB activation. Furthermore, a key UPR initiator, IRE1, acts to maintain IKK basal activity through IRE1's kinase, but not RNase, activity. Inputs from IRE1 and IKK, in combination with translation repression by PERK, another UPR initiator, lead to maximal NF-κB activation during the UPR. These interdependencies have a significant impact in cancer cells with elevated IKK/NF-κB activity such as renal cell carcinoma cells (786-0). Inhibition of IKK by an IKK inhibitor, which significantly decreases NF-κB activity, is overridden by UPR induction, arguing for the importance of considering UPR activation in cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
HCV induces transforming growth factor β1 through activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 1;6:22487. doi: 10.1038/srep22487. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26927933 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;26(8):3071-84. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.8.3071-3084.2006. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16581782 Free PMC article.
-
Coordination between Two Branches of the Unfolded Protein Response Determines Apoptotic Cell Fate.Mol Cell. 2018 Aug 16;71(4):629-636.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.038. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30118681
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress sensing in the unfolded protein response.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Mar 1;5(3):a013169. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a013169. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23388626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensing endoplasmic reticulum stress.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;738:153-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-1680-7_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22399379 Review.
Cited by
-
The unfolded protein response in immunity and inflammation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Aug;16(8):469-84. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.62. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27346803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-a key guardian in cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jul 30;10(1):343. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02110-3. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39080273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of action of amyloid-beta and its precursor protein in neuronal cell death.Metab Brain Dis. 2020 Jan;35(1):11-30. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00516-y. Epub 2019 Dec 6. Metab Brain Dis. 2020. PMID: 31811496 Review.
-
Virus and tumor microenvironment induced ER stress and unfolded protein response: from complexity to therapeutics.Oncotarget. 2018 Aug 7;9(61):31920-31936. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25886. eCollection 2018 Aug 7. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30159133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RAGE/NF-κB pathway mediates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in alveolar type I epithelial cells isolated from neonate rats.Inflammation. 2014 Oct;37(5):1623-9. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9889-y. Inflammation. 2014. PMID: 24740410
References
-
- Mori K (2000) Tripartite management of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 101: 451–454. - PubMed
-
- Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 519–529. - PubMed
-
- Romero-Ramirez L, Cao H, Nelson D, Hammond E, Lee AH, et al. (2004) XBP1 is essential for survival under hypoxic conditions and is required for tumor growth. Cancer Res 64: 5943–5947. - PubMed

