Educational application for visualization and analysis of electric field strength in multiple electrode electroporation
- PMID: 23107609
- PMCID: PMC3528424
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6920-12-102
Educational application for visualization and analysis of electric field strength in multiple electrode electroporation
Abstract
Background: Electrochemotherapy is a local treatment that utilizes electric pulses in order to achieve local increase in cytotoxicity of some anticancer drugs. The success of this treatment is highly dependent on parameters such as tissue electrical properties, applied voltages and spatial relations in placement of electrodes that are used to establish a cell-permeabilizing electric field in target tissue. Non-thermal irreversible electroporation techniques for ablation of tissue depend similarly on these parameters. In the treatment planning stage, if oversimplified approximations for evaluation of electric field are used, such as U/d (voltage-to-distance ratio), sufficient field strength may not be reached within the entire target (tumor) area, potentially resulting in treatment failure.
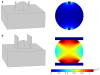
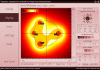
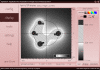
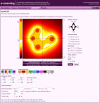
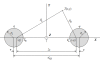
Results: In order to provide an aid in education of medical personnel performing electrochemotherapy and non-thermal irreversible electroporation for tissue ablation, assist in visualizing the electric field in needle electrode electroporation and the effects of changes in electrode placement, an application has been developed both as a desktop- and a web-based solution. It enables users to position up to twelve electrodes in a plane of adjustable dimensions representing a two-dimensional slice of tissue. By means of manipulation of electrode placement, i.e. repositioning, and the changes in electrical parameters, the users interact with the system and observe the resulting electrical field strength established by the inserted electrodes in real time. The field strength is calculated and visualized online and instantaneously reflects the desired changes, dramatically improving the user friendliness and educational value, especially compared to approaches utilizing general-purpose numerical modeling software, such as finite element modeling packages.
Conclusion: In this paper we outline the need and offer a solution in medical education in the field of electroporation-based treatments, e.g. primarily electrochemotherapy and non-thermal irreversible tissue ablation. We present the background, the means of implementation and the fully functional application, which is the first of its kind. While the initial feedback from students that have evaluated this application as part of an e-learning course is positive, a formal study is planned to thoroughly evaluate the current version and identify possible future improvements and modifications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An e-learning application on electrochemotherapy.Biomed Eng Online. 2009 Oct 20;8:26. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-8-26. Biomed Eng Online. 2009. PMID: 19843322 Free PMC article.
-
Analytical and numerical quantification and comparison of the local electric field in the tissue for different electrode configurations.Biomed Eng Online. 2007 Oct 15;6:37. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-6-37. Biomed Eng Online. 2007. PMID: 17937793 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of electric field distribution in tissues during electroporation.Biomed Eng Online. 2013 Feb 21;12:16. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-12-16. Biomed Eng Online. 2013. PMID: 23433433 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemotherapy: technological advancements for efficient electroporation-based treatment of internal tumors.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2012 Dec;50(12):1213-25. doi: 10.1007/s11517-012-0991-8. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2012. PMID: 23179413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applicator and electrode design for in vivo DNA delivery by electroporation.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;423:35-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-194-9_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18370189 Review.
Cited by
-
Education on electrical phenomena involved in electroporation-based therapies and treatments: a blended learning approach.Biomed Eng Online. 2016 Apr 7;15:36. doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0152-7. Biomed Eng Online. 2016. PMID: 27056369 Free PMC article.
-
OpenEP: an open-source simulator for electroporation-based tumor treatments.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 14;11(1):1423. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-79858-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33446750 Free PMC article.
-
Planning of electroporation-based treatments using Web-based treatment-planning software.J Membr Biol. 2013 Nov;246(11):833-42. doi: 10.1007/s00232-013-9567-2. Epub 2013 Jun 19. J Membr Biol. 2013. PMID: 23780414
-
PIRET-A Platform for Treatment Planning in Electroporation-Based Therapies.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023 Jun;70(6):1902-1910. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2022.3232038. Epub 2023 May 19. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 37015676 Free PMC article.
-
EView: An electric field visualization web platform for electroporation-based therapies.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020 Dec;197:105682. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105682. Epub 2020 Aug 2. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020. PMID: 32795723 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

