STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner
- PMID: 23104886
- PMCID: PMC3530905
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635
STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner
Abstract
Motivation: Accurate alignment of high-throughput RNA-seq data is a challenging and yet unsolved problem because of the non-contiguous transcript structure, relatively short read lengths and constantly increasing throughput of the sequencing technologies. Currently available RNA-seq aligners suffer from high mapping error rates, low mapping speed, read length limitation and mapping biases.
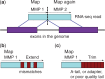
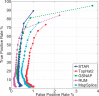
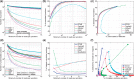
Results: To align our large (>80 billon reads) ENCODE Transcriptome RNA-seq dataset, we developed the Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) software based on a previously undescribed RNA-seq alignment algorithm that uses sequential maximum mappable seed search in uncompressed suffix arrays followed by seed clustering and stitching procedure. STAR outperforms other aligners by a factor of >50 in mapping speed, aligning to the human genome 550 million 2 × 76 bp paired-end reads per hour on a modest 12-core server, while at the same time improving alignment sensitivity and precision. In addition to unbiased de novo detection of canonical junctions, STAR can discover non-canonical splices and chimeric (fusion) transcripts, and is also capable of mapping full-length RNA sequences. Using Roche 454 sequencing of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction amplicons, we experimentally validated 1960 novel intergenic splice junctions with an 80-90% success rate, corroborating the high precision of the STAR mapping strategy.
Availability and implementation: STAR is implemented as a standalone C++ code. STAR is free open source software distributed under GPLv3 license and can be downloaded from http://code.google.com/p/rna-star/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mapping RNA-seq Reads with STAR.Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015 Sep 3;51:11.14.1-11.14.19. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1114s51. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26334920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing RNA-Seq Mapping with STAR.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1415:245-62. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3572-7_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27115637
-
Supersplat--spliced RNA-seq alignment.Bioinformatics. 2010 Jun 15;26(12):1500-5. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq206. Epub 2010 Apr 21. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20410051 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of RNA-Seq alignment algorithms and the RNA-Seq unified mapper (RUM).Bioinformatics. 2011 Sep 15;27(18):2518-28. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr427. Epub 2011 Jul 19. Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21775302 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping RNA-seq reads to transcriptomes efficiently based on learning to hash method.Comput Biol Med. 2020 Jan;116:103539. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103539. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Comput Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 31765913 Review.
Cited by
-
Inversions encounter relaxed genetic constraints and balance birth and death of TPS genes in Curcuma.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 29;15(1):9349. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53719-y. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39472560 Free PMC article.
-
Microprotein-encoding RNA regulation in cells treated with pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrotic stimuli.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 5;25(1):1034. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10948-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39497054 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Rat Osteosarcoma Cell Line UMR-106 by Long-Read Technologies Identifies a Large Block of Amplified Genes Associated with Human Disease.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 26;15(10):1254. doi: 10.3390/genes15101254. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457378 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between Two Paralogous Human Silencing Hub (HuSH) Complexes in Regulating LINE-1 Element Silencing.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 3;15(1):9492. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53761-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39489739 Free PMC article.
-
A spatiotemporal transcriptomic atlas of mouse placentation.Cell Discov. 2024 Oct 22;10(1):110. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00740-6. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 39438452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Bona F, et al. Optimal spliced alignments of short sequence reads. Bioinformatics. 2008;24:i174–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

