Solid-phase glycan isolation for glycomics analysis
- PMID: 23090885
- PMCID: PMC3674833
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201200045
Solid-phase glycan isolation for glycomics analysis
Abstract
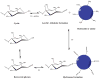
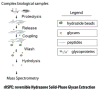
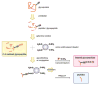
Glycosylation is one of the most significant protein PTMs. The biological activities of proteins are dramatically changed by the glycans associated with them. Thus, structural analysis of the glycans of glycoproteins in complex biological or clinical samples is critical in correlation with the functions of glycans with diseases. Profiling of glycans by HPLC-MS is a commonly used technique in analyzing glycan structures and quantifying their relative abundance in different biological systems. Methods relied on MS require isolation of glycans from negligible salts and other contaminant ions since salts and ions may interfere with the glycans, resulting in poor glycan ionization. To accomplish those objectives, glycan isolation and clean-up methods including SPE, liquid-phase extraction, chromatography, and electrophoresis have been developed. Traditionally, glycans are isolated from proteins or peptides using a combination of hydrophobic and hydrophilic columns: proteins and peptides remain on hydrophobic absorbent while glycans, salts, and other hydrophilic reagents are collected as flowthrough. The glycans in the flowthrough are then purified through graphite-activated carbon column by hydrophilic interaction LC. Yet, the drawback in these affinity-based approaches is nonspecific binding. As a result, chemical methods by hydrazide or oxime have been developed for solid-phase isolation of glycans with high specificity and yield. Combined with high-resolution MS, specific glycan isolation techniques provide tremendous potentials as useful tools for glycomics analysis.
© 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Applications of chromatography in glycomics].Se Pu. 2024 Jul;42(7):646-657. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1123.2023.12003. Se Pu. 2024. PMID: 38966973 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Quantitative O-glycomics based on improvement of the one-pot method for nonreductive O-glycan release and simultaneous stable isotope labeling with 1-(d0/d5)phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone followed by mass spectrometric analysis.J Proteomics. 2017 Jan 6;150:18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.08.012. Epub 2016 Aug 29. J Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 27585995
-
A Quantitative Glycomics and Proteomics Combined Purification Strategy.J Vis Exp. 2016 Mar 8;(109):53735. doi: 10.3791/53735. J Vis Exp. 2016. PMID: 27023253 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoenzymatic method for glycomics: Isolation, identification, and quantitation.Proteomics. 2016 Jan;16(2):241-56. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201500266. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26390280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Permethylated Glycan by Liquid Chromatography (LC) and Mass Spectrometry (MS).Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1503:83-96. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6493-2_7. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27743360 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glycomic analysis using glycoprotein immobilization for glycan extraction.Anal Chem. 2013 Jun 4;85(11):5555-61. doi: 10.1021/ac400761e. Epub 2013 May 20. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23688297 Free PMC article.
-
Glycomic analysis by glycoprotein immobilization for glycan extraction and liquid chromatography on microfluidic chip.Anal Chem. 2013 Nov 5;85(21):10117-25. doi: 10.1021/ac4013013. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Anal Chem. 2013. PMID: 24111616 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Cell Glycocalyx with Mass Spectrometry Methods.Cells. 2019 Aug 13;8(8):882. doi: 10.3390/cells8080882. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31412618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycomics studies using sialic acid derivatization and mass spectrometry.Nat Rev Chem. 2020 May;4(5):229-242. doi: 10.1038/s41570-020-0174-3. Epub 2020 Mar 17. Nat Rev Chem. 2020. PMID: 37127981 Review.
-
Urine lipoarabinomannan glycan in HIV-negative patients with pulmonary tuberculosis correlates with disease severity.Sci Transl Med. 2017 Dec 13;9(420):eaal2807. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aal2807. Sci Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29237757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Freeze HH, Stanley P, Bertozzi CR, Hart GW, Etzler ME, editors. Essentials of Glycobiology. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; NY: 2009. - PubMed
-
- Krueger KE, Srivastava S. Posttranslational protein modifications. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1799–1810. - PubMed
-
- Sönmez H, Öztürk ZG, Ulutin T, Domaniç N, et al. Carbohydrate-deficient transferrin and sialidase levels in coronary heart disease. Thromb Res. 2000;99:311–315. - PubMed
-
- Endo T, Manya H. O-Mannosylation in Mammalian Cells. Humana Press Inc; Totowa, NJ: 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

