The NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase SIRT6 promotes cytokine production and migration in pancreatic cancer cells by regulating Ca2+ responses
- PMID: 23086953
- PMCID: PMC3510797
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.405837
The NAD+-dependent histone deacetylase SIRT6 promotes cytokine production and migration in pancreatic cancer cells by regulating Ca2+ responses
Abstract
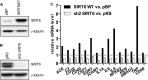
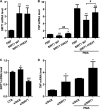
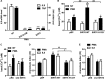
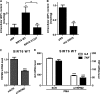
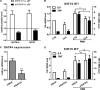
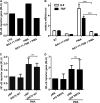
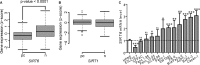
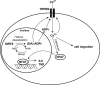
Cytokine secretion by cancer cells contributes to cancer-induced symptoms and angiogenesis. Studies show that the sirtuin SIRT6 promotes inflammation by enhancing TNF expression. Here, we aimed to determine whether SIRT6 is involved in conferring an inflammatory phenotype to cancer cells and to define the mechanisms linking SIRT6 to inflammation. We show that SIRT6 enhances the expression of pro-inflammatory cyto-/chemokines, such as IL8 and TNF, and promotes cell migration in pancreatic cancer cells by enhancing Ca(2+) responses. Via its enzymatic activity, SIRT6 increases the intracellular levels of ADP-ribose, an activator of the Ca(2+) channel TRPM2. In turn, TRPM2 and Ca(2+) are shown to be involved in SIRT6-induced TNF and IL8 expression. SIRT6 increases the nuclear levels of the Ca(2+)-dependent transcription factor, nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT), and cyclosporin A, a calcineurin inhibitor that reduces NFAT activity, reduces TNF and IL8 expression in SIRT6-overexpressing cells. These results implicate a role for SIRT6 in the synthesis of Ca(2+)-mobilizing second messengers, in the regulation of Ca(2+)-dependent transcription factors, and in the expression of pro-inflammatory, pro-angiogenic, and chemotactic cytokines. SIRT6 inhibition may help combat cancer-induced inflammation, angiogenesis, and metastasis.
Figures
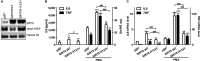
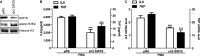
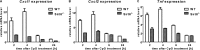
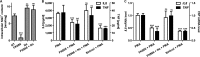
Similar articles
-
Sirtuin-6 deficiency exacerbates diabetes-induced impairment of wound healing.Exp Dermatol. 2015 Oct;24(10):773-8. doi: 10.1111/exd.12762. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26010430 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory properties of sirtuin 6 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:597514. doi: 10.1155/2012/597514. Epub 2012 Oct 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 23132960 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT6 deacetylase activity regulates NAMPT activity and NAD(P)(H) pools in cancer cells.FASEB J. 2019 Mar;33(3):3704-3717. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800321R. Epub 2018 Dec 4. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30514106 Free PMC article.
-
Biological and catalytic functions of sirtuin 6 as targets for small-molecule modulators.J Biol Chem. 2020 Aug 7;295(32):11021-11041. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.011438. Epub 2020 Jun 9. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32518153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Sirtuin 6 in the Deacetylation of Histone Proteins as a Factor in the Progression of Neoplastic Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 29;25(1):497. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010497. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203666 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The TRPM2 ion channel regulates metabolic and thermogenic adaptations in adipose tissue of cold-exposed mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 6;14:1251351. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1251351. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38390373 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation into an Effector Memory Phenotype Potentiates HIV-1 Latency Reversal in CD4+ T Cells.J Virol. 2019 Nov 26;93(24):e00969-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00969-19. Print 2019 Dec 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 31578289 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Sirtuins in Tumor Angiogenesis.Front Oncol. 2020 Jan 17;9:1516. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01516. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32010617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRPM2 in Cancer.Cell Calcium. 2019 Jun;80:8-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Cell Calcium. 2019. PMID: 30925291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transportome Malfunctions and the Hallmarks of Pancreatic Cancer.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;181:105-127. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_20. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32770395 Review.
References
-
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R. A. (2011) Hallmarks of cancer. The next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F. R., Mantovani A. (2012) Cancer-related inflammation. Common themes and therapeutic opportunities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 22, 33–40 - PubMed
-
- Mantovani A. (2010) Molecular pathways linking inflammation and cancer. Curr. Mol. Med. 10, 369–373 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

