Characterization of an early passage Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cell line, MS-1, and its growth in NOD scid gamma mice
- PMID: 23085629
- PMCID: PMC3606892
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2012.10.001
Characterization of an early passage Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cell line, MS-1, and its growth in NOD scid gamma mice
Abstract
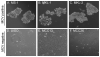
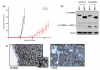
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive skin cancer with a high mortality rate. The majority of MCC (70-80%) harbor clonally integrated Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) in the tumor genome and express viral T antigen oncoproteins. The characterization of an early passage MCV-positive MCC cell line MS-1 is described, and its cellular, immunohistochemical, and virological features to MCV-negative (UISO, MCC13, and MCC26) and MCV-positive cell lines (MKL-1 and MKL-2) were compared. The MS-1 cellular genome harbors integrated MCV, which preserves an identical viral sequence from its parental tumor. Neither VP2 gene transcripts nor VP1 protein are detectable in MS-1 or other MCV-positive MCC cell lines tested. Mapping of viral and cellular integration sites in MS-1 and MCC tumor samples demonstrates no consistent viral or cellular gene integration locus. All MCV-positive cell lines show cytokeratin 20 positivity and grow in suspension. When injected subcutaneously into NOD scid gamma (NSG) mice, MS-1 forms a discrete macroscopic tumor. Immunophenotypic analysis of the MS-1 cell line and xenografts in mice show identical profiles to the parental tumor biopsy. Hence, MS-1 is an early passage cell line that provides a useful in vitro model to characterize MCV-positive MCC.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cells do not require expression of the viral small T antigen.J Invest Dermatol. 2013 Aug;133(8):2059-64. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.82. Epub 2013 Feb 25. J Invest Dermatol. 2013. PMID: 23439392
-
Survivin is a therapeutic target in Merkel cell carcinoma.Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 9;4(133):133ra56. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003713. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22572880 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of six Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cell lines: Integration pattern suggest that large T antigen truncating events occur before or during integration.Int J Cancer. 2019 Aug 15;145(4):1020-1032. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32280. Epub 2019 Apr 4. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30873613
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus: a newly discovered human virus with oncogenic potential.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):118-30. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.029. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus: Oncogenesis in a Stable Genome.Viruses. 2021 Dec 30;14(1):58. doi: 10.3390/v14010058. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 35062263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ALK is frequently phosphorylated in Merkel cell carcinoma and associates with longer survival.PLoS One. 2021 May 24;16(5):e0252099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252099. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34029351 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell carcinoma: updates in tumor biology, emerging therapies, and preclinical models.Front Oncol. 2024 Jul 29;14:1413793. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1413793. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39136002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response of Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive merkel cell carcinoma xenografts to a survivin inhibitor.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 18;8(11):e80543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080543. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260412 Free PMC article.
-
MCV Truncated Large T antigen interacts with BRD4 in tumors.Matters (Zur). 2019 Jan 11;2019:10.19185/matters.201811000004. doi: 10.19185/matters.201811000004. Matters (Zur). 2019. PMID: 32395462 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Merkel Cell Carcinoma by Engineered T Cells Specific to T-Antigens of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Aug 1;24(15):3644-3655. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2661. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29669806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agelli M, Clegg LX. Epidemiology of primary Merkel cell carcinoma in the United States. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003;49:832–841. - PubMed
-
- Allen PJ, Bowne WB, Jaques DP, Brennan MF, Busam K, Coit DG. Merkel cell carcinoma: prognosis and treatment of patients from a single institution. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005;23:2300–2309. - PubMed
-
- Becker JC, Houben R, Ugurel S, Trefzer U, Pfohler C, Schrama D. MC polyomavirus is frequently present in Merkel cell carcinoma of European patients. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2009;129:248–250. - PubMed
-
- Busam KJ, Jungbluth AA, Rekthman N, Coit D, Pulitzer M, Bini J, Arora R, Hanson NC, Tassello JA, Frosina D, Moore P, Chang Y. Merkel cell polyomavirus expression in Merkel cell carcinomas and its absence in combined tumors and pulmonary neuroendocrine carcinomas. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009;33:1378–1385. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carney DN, Gazdar AF, Bepler G, Guccion JG, Marangos PJ, Moody TW, Zweig MH, Minna JD. Establishment and identification of small cell lung cancer cell lines having classic and variant features. Cancer Res. 1985;45:2913–2923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

