Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and interleukin (IL)-1β synergistically promote ERK1/2-mediated invasive breast ductal cancer cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 23083134
- PMCID: PMC3537707
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-11-79
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and interleukin (IL)-1β synergistically promote ERK1/2-mediated invasive breast ductal cancer cell migration and invasion
Abstract
Background: Patients with invasive breast ductal carcinoma (IBDC) with metastasis have a very poor prognosis. Little is known about the synergistic action of growth and inflammatory factors in IBDC metastases.
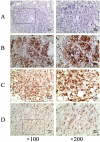
Methods: The expression of activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (phosphorylated or p-ERK1/2) was analyzed by immunohistochemistry in IBDC tissue samples from 80 cases. BT474 IBDC cell migration and invasion were quantified using the Transwell assay. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 expression and activity were analyzed by RT-PCR, Western blotting and zymography. Activator protein (AP)-1 activity was measured with a luciferase reporter gene assay. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test, Chi-square test, the partition of Chi-square test, independent t-test, and Spearman's method were used for the statistical analysis.
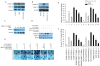
Results: Phosphorylated ERK1/2 was detected in 58/80 (72.5%) IBDC tissues, and was associated with higher TNM stage and lymph node metastasis, but not patient age or tumor size. Individually, epidermal growth factor (EGF), and interleukin (IL)-1β activated ERK1/2, increased cell migration and invasion, MMP-9 expression and activity, AP-1 activation in vitro and the expression of p-ERK1/2 was positively correlated with EGF expression levels, as well as IL-1β, MMP-9 and c-fos in IBDC tissue samples. Co-stimulation with EGF and IL-1β synergistically increased ERK1/2 and AP-1 activation, cell migration and invasion, and MMP-9 expression and activity. Inhibition of ERK1/2 using U0126 or siRNA abolished EGF and/or IL-1β-induced cell migration and invasion in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Activated ERK1/2 was associated with higher TNM stage and lymph node metastasis in IBDC. Both in vitro and in vivo studies indicated that ERK-1/2 activation may increase the metastatic ability of IBDC cells. Growth and inflammatory factors synergistically induced IBDC cell migration and invasion via ERK1/2 signaling, AP-1 activation and MMP-9 upregulation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Additive effects of EGF and IL-1β regulate tumor cell migration and invasion in gastric adenocarcinoma via activation of ERK1/2.Int J Oncol. 2014 Jul;45(1):291-301. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2401. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24789460
-
IL-1β promotes corneal epithelial cell migration by increasing MMP-9 expression through NF-κB- and AP-1-dependent pathways.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57955. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057955. Epub 2013 Mar 7. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23505448 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1β-induced activation of p38 promotes metastasis in gastric adenocarcinoma via upregulation of AP-1/c-fos, MMP2 and MMP9.Mol Cancer. 2014 Jan 31;13:18. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-18. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24479681 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17 stimulates MMP-1 expression in primary human cardiac fibroblasts via p38 MAPK- and ERK1/2-dependent C/EBP-beta , NF-kappaB, and AP-1 activation.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Dec;293(6):H3356-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00928.2007. Epub 2007 Oct 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17921324
-
Chrysin inhibits tumor promoter-induced MMP-9 expression by blocking AP-1 via suppression of ERK and JNK pathways in gastric cancer cells.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 15;10(4):e0124007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124007. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25875631 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Amphiregulin regulates proliferation and migration of HER2-positive breast cancer cells.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018 Apr;41(2):159-168. doi: 10.1007/s13402-017-0363-3. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2018. PMID: 29181633
-
Involvement of SLC39A6 in gastric adenocarcinoma and correlation of the SLC39A6 polymorphism rs1050631 with clinical outcomes after resection.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 8;19(1):1069. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6222-z. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31703635 Free PMC article.
-
Diverging inflammasome signals in tumorigenesis and potential targeting.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Apr;19(4):197-214. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0123-y. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30842595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contrasting roles of inflammasomes in cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2018 Apr 1;8(4):566-583. eCollection 2018. Am J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29736304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-1 drives breast cancer growth and bone metastasis in vivo.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 15;7(46):75571-75584. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12289. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27765923 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

