c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic regulator
- PMID: 23070002
- PMCID: PMC4817998
c-FLIP, a master anti-apoptotic regulator
Abstract
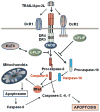
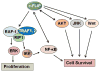
Cellular FLICE (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein (c-FLIP) is a master anti-apoptotic regulator and resistance factor that suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), Fas-L, and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis, as well as apoptosis triggered by chemotherapy agents in malignant cells. c-FLIP is expressed as long (c-FLIP(L)), short (c-FLIP(S)), and c-FLIP(R) splice variants in human cells. c-FLIP binds to FADD and/or caspase-8 or -10 and TRAIL receptor 5 (DR5) in a ligand-dependent and -independent fashion and forms an apoptosis inhibitory complex (AIC). This interaction in turn prevents death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) formation and subsequent activation of the caspase cascade. c-FLIP(L) and c-FLIP(S) are also known to have multifunctional roles in various signaling pathways, as well as activating and/or upregulating several cytoprotective and pro-survival signaling proteins including Akt, ERK, and NF-kB. Upregulation of c-FLIP has been found in various tumor types, and its silencing has been shown to restore apoptosis triggered by cytokines and various chemotherapeutic agents. Hence, c-FLIP is an important target for cancer therapy. For example, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) that specifically knockdown the expression of c-FLIP(L) in diverse human cancer cell lines augmented TRAIL-induced DISC recruitment and increased the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents, thereby enhancing effector caspase stimulation and apoptosis. Moreover, small molecules causing degradation of c-FLIP as well as decreasing mRNA and protein levels of c-FLIP(L) and c-FLIP(S) splice variants have been found, and much effort is focused on developing other c-FLIP-targeted cancer therapies. This review focuses on (1) the anti-apoptotic role of c-FLIP splice variants in preventing apoptosis and inducing cytokine and chemotherapy drug resistance, (2) the molecular mechanisms and factors that regulate c-FLIP expression, and (3) modulation of c-FLIP expression and function to eliminate cancer cells or increase the efficacy of anticancer agents. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled "Apoptosis: Four Decades Later".
Figures
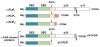
Similar articles
-
Targeting the Anti-Apoptotic Protein c-FLIP for Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2011 Jun;3(2):1639-71. doi: 10.3390/cancers3021639. Cancers (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22348197 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (C-FLIP): a novel target for cancer therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008 Feb;8(1):37-46. doi: 10.2174/156800908783497087. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 18288942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-FLIP knockdown induces ligand-independent DR5-, FADD-, caspase-8-, and caspase-9-dependent apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2008 Dec 15;76(12):1694-704. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.09.007. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Biochem Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18840411 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of c-FLIP in Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Autophagy.J Carcinog Mutagen. 2013;Suppl 6:003. doi: 10.4172/2157-2518.S6-003. J Carcinog Mutagen. 2013. PMID: 25379355 Free PMC article.
-
Down-regulation of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins, particularly c-FLIP by therapeutic agents; the novel view to overcome resistance to TRAIL.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Oct;233(10):6470-6485. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26585. Epub 2018 May 9. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29741767 Review.
Cited by
-
A delay prior to mitotic entry triggers caspase 8-dependent cell death in p53-deficient Hela and HCT-116 cells.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(7):1070-81. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1007781. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25602147 Free PMC article.
-
Down Regulation of c-FLIPL Enhance PD-1 Blockade Efficacy in B16 Melanoma.Front Oncol. 2019 Sep 4;9:857. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00857. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31552181 Free PMC article.
-
The pro-survival function of DLEC1 and its protection of cancer cells against 5-FU-induced apoptosis through up-regulation of BCL-XL.Cytotechnology. 2019 Feb;71(1):23-33. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0258-9. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Cytotechnology. 2019. PMID: 30607648 Free PMC article.
-
The Endless Saga of Monocyte Diversity.Front Immunol. 2019 Aug 6;10:1786. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01786. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31447834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subendothelial matrix components influence endothelial cell apoptosis in vitro.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb 1;316(2):C210-C222. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00005.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30566394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cereghetti GM, Scorrano L. The many shapes of mitochondrial death. Oncogene. 2006;25:4717–24. - PubMed
-
- Gogvadze V, Orrenius S. Mitochondrial regulation of apoptotic cell death. Chem Biol Interact. 2006;163:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Meng XW, Lee S, Kaufmann SH. Apoptosis in the treatment of cancer: A promise kept? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:668–76. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, et al. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: Requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell. 1996;86:147–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
