Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2 (Shp2) is a component of the A-kinase-anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc complex and is inhibited by protein kinase A (PKA) under pathological hypertrophic conditions in the heart
- PMID: 23045525
- PMCID: PMC3504768
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.385641
Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase 2 (Shp2) is a component of the A-kinase-anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc complex and is inhibited by protein kinase A (PKA) under pathological hypertrophic conditions in the heart
Abstract
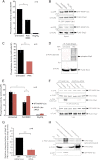
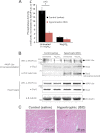
Background: AKAP-Lbc is a scaffold protein that coordinates cardiac hypertrophic signaling.
Results: AKAP-Lbc interacts with Shp2, facilitating its regulation by PKA.
Conclusion: AKAP-Lbc integrates PKA and Shp2 signaling in the heart. Under pathological hypertrophic conditions Shp2 is phosphorylated by PKA, and phosphatase activity is inhibited.
Significance: Inhibition of Shp2 activity through AKAP-Lbc-anchored PKA is a previously unrecognized mechanism that may promote pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Pathological cardiac hypertrophy (an increase in cardiac mass resulting from stress-induced cardiac myocyte growth) is a major factor underlying heart failure. Our results identify a novel mechanism of Shp2 inhibition that may promote cardiac hypertrophy. We demonstrate that the tyrosine phosphatase, Shp2, is a component of the A-kinase-anchoring protein (AKAP)-Lbc complex. AKAP-Lbc facilitates PKA phosphorylation of Shp2, which inhibits its protein-tyrosine phosphatase activity. Given the important cardiac roles of both AKAP-Lbc and Shp2, we investigated the AKAP-Lbc-Shp2 interaction in the heart. AKAP-Lbc-tethered PKA is implicated in cardiac hypertrophic signaling; however, mechanism of PKA action is unknown. Mutations resulting in loss of Shp2 catalytic activity are also associated with cardiac hypertrophy and congenital heart defects. Our data indicate that AKAP-Lbc integrates PKA and Shp2 signaling in the heart and that AKAP-Lbc-associated Shp2 activity is reduced in hypertrophic hearts in response to chronic β-adrenergic stimulation and PKA activation. Thus, while induction of cardiac hypertrophy is a multifaceted process, inhibition of Shp2 activity through AKAP-Lbc-anchored PKA is a previously unrecognized mechanism that may promote compensatory cardiac hypertrophy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protein Kinase A (PKA) Phosphorylation of Shp2 Protein Inhibits Its Phosphatase Activity and Modulates Ligand Specificity.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 8;290(19):12058-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.642983. Epub 2015 Mar 23. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25802336 Free PMC article.
-
The C-terminus of the long AKAP13 isoform (AKAP-Lbc) is critical for development of compensatory cardiac hypertrophy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014 Jan;66:27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.10.010. Epub 2013 Oct 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24161911 Free PMC article.
-
Anchoring of both PKA and 14-3-3 inhibits the Rho-GEF activity of the AKAP-Lbc signaling complex.EMBO J. 2004 Jul 21;23(14):2811-20. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600287. Epub 2004 Jul 1. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15229649 Free PMC article.
-
AKAP-Lbc: a molecular scaffold for the integration of cyclic AMP and Rho transduction pathways.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):603-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16460837 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
Cited by
-
UCR1C is a novel activator of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) long isoforms and attenuates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.Cell Signal. 2015 May;27(5):908-22. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Feb 12. Cell Signal. 2015. PMID: 25683917 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac function modulation depends on the A-kinase anchoring protein complex.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Nov;23(11):7170-7179. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14659. Epub 2019 Sep 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31512389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD99-Derived Agonist Ligands Inhibit Fibronectin-Induced Activation of β1 Integrin through the Protein Kinase A/SHP2/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase/PTPN12/Focal Adhesion Kinase Signaling Pathway.Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 29;37(14):e00675-16. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00675-16. Print 2017 Jul 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28483911 Free PMC article.
-
Repeated Mu-Opioid Exposure Induces a Novel Form of the Hyperalgesic Priming Model for Transition to Chronic Pain.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 9;35(36):12502-17. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1673-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26354917 Free PMC article.
-
The crystal structure of the RhoA-AKAP-Lbc DH-PH domain complex.Biochem J. 2014 Dec 1;464(2):231-9. doi: 10.1042/BJ20140606. Biochem J. 2014. PMID: 25186459 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

