Crystal structure of adenovirus E3-19K bound to HLA-A2 reveals mechanism for immunomodulation
- PMID: 23042604
- PMCID: PMC3492506
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2396
Crystal structure of adenovirus E3-19K bound to HLA-A2 reveals mechanism for immunomodulation
Abstract
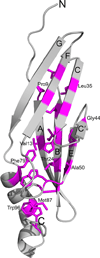
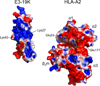
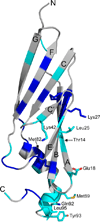
E3-19K binds to and retains MHC class I molecules in the endoplasmic reticulum, suppressing anti-adenovirus activities of T cells. We determined the structure of the adenovirus serotype 2 (Ad2, species C) E3-19K-HLA-A2 complex to 1.95-Å resolution. Ad2 E3-19K binds to the N terminus of the HLA-A2 groove, contacting the α1, α2 and α3 domains and β(2)m. Ad2 E3-19K has a unique structure comprising a large N-terminal domain, formed by two partially overlapping β-sheets arranged in a V shape, and a C-terminal α-helix and tail. The structure reveals determinants in E3-19K and HLA-A2 that are important for complex formation; conservation of some of these determinants in E3-19K proteins of different species and MHC I molecules of different loci suggests a universal binding mode for all E3-19K proteins. Our structure is important for understanding the immunomodulatory function of E3-19K.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure of the Adenovirus Type 4 (Species E) E3-19K/HLA-A2 Complex Reveals Species-Specific Features in MHC Class I Recognition.J Immunol. 2016 Aug 15;197(4):1399-407. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600541. Epub 2016 Jul 6. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27385781 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) lumenal-domain of the adenovirus serotype 2 E3-19K protein for association with and ER-retention of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules.Mol Immunol. 2011 Jan;48(4):532-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2010.10.017. Epub 2010 Nov 20. Mol Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21094528 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of class I MHC regions which bind to the adenovirus E3-19k protein.Mol Immunol. 1994 Nov;31(16):1277-84. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)90078-7. Mol Immunol. 1994. PMID: 7969188
-
Tumor necrosis factor alpha increases expression of adenovirus E3 proteins.Immunobiology. 1995 Jul;193(2-4):186-92. doi: 10.1016/s0171-2985(11)80542-5. Immunobiology. 1995. PMID: 8530142 Review.
-
Association of intracellular proteins with folded major histocompatibility complex class I molecules.Immunol Res. 2004;30(2):171-9. doi: 10.1385/IR:30:2:171. Immunol Res. 2004. PMID: 15477658 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure of the Adenovirus Type 4 (Species E) E3-19K/HLA-A2 Complex Reveals Species-Specific Features in MHC Class I Recognition.J Immunol. 2016 Aug 15;197(4):1399-407. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600541. Epub 2016 Jul 6. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27385781 Free PMC article.
-
Cowpox virus employs a two-pronged strategy to outflank MHCI antigen presentation.Mol Immunol. 2013 Sep;55(2):156-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.11.011. Epub 2013 Jan 10. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23312338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tapasin-mediated editing of the MHC I immunopeptidome is epitope specific and dependent on peptide off-rate, abundance, and level of tapasin expression.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 31;13:956603. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.956603. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36389776 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel MHC-I Surface Targeted for Binding by the MCMV m06 Immunoevasin Revealed by Solution NMR.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 27;290(48):28857-68. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.689661. Epub 2015 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26463211 Free PMC article.
-
The SPPL3-Defined Glycosphingolipid Repertoire Orchestrates HLA Class I-Mediated Immune Responses.Immunity. 2021 Jan 12;54(1):132-150.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 33271119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berk AJ. Adenoviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, editors. Fields Virology. 5th. Philadelphia: Lipincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2395–2436.
-
- Wold WSM, Horwitz MS. Adenoviridae: The viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, editors. Fields Virology. 5th. Philadelphia: Lipincott Williams & Wilkins; 2007. pp. 2355–2394.
-
- Hansen TH, Bouvier M. MHC class I antigen presentation: learning from viral evasion strategies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009;9:503–513. - PubMed
-
- Burgert H-G, Ruzsics Z, Obermeier S, Hilgendorf A, Windheim M, Elsing A. Subversion of host defense mechanisms by Adenoviruses. In: Koszinowski UH, Hengel H, editors. Viral Proteins Counteracting Host Defenses. Berlin: Springer-Verlag; 2002. pp. 273–318. - PubMed
-
- Andersson M, Paabo S, Nilsson T, Peterson PA. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985;43:215–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

