Pathological role of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in adverse ventricular remodeling
- PMID: 23019294
- PMCID: PMC3484211
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.115592
Pathological role of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 in adverse ventricular remodeling
Abstract
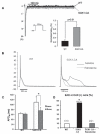
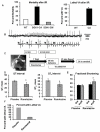
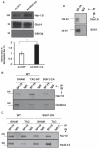
Background: Heart failure is a growing cause of morbidity and mortality. Cardiac phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling promotes cardiomyocyte survival and function, but it is paradoxically activated in heart failure, suggesting that chronic activation of this pathway may become maladaptive. Here, we investigated the downstream phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase effector, serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase-1 (SGK1), in heart failure and its complications.
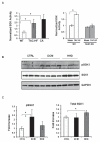
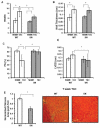
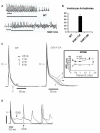
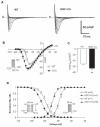
Methods and results: We found that cardiac SGK1 is activated in human and murine heart failure. We investigated the role of SGK1 in the heart by using cardiac-specific expression of constitutively active or dominant-negative SGK1. Cardiac-specific activation of SGK1 in mice increased mortality, cardiac dysfunction, and ventricular arrhythmias. The proarrhythmic effects of SGK1 were linked to biochemical and functional changes in the cardiac sodium channel and could be reversed by treatment with ranolazine, a blocker of the late sodium current. Conversely, cardiac-specific inhibition of SGK1 protected mice after hemodynamic stress from fibrosis, heart failure, and sodium channel alterations.
Conclusions: SGK1 appears both necessary and sufficient for key features of adverse ventricular remodeling and may provide a novel therapeutic target in cardiac disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
Adverse cardiac remodeling: phosphoinositide 3-kinase, another unique factor in a multifactorial condition.Circulation. 2012 Oct 30;126(18):2175-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.138313. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 23019295 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Phosphorylation at Ser571 Regulates Late Current, Arrhythmia, and Cardiac Function In Vivo.Circulation. 2015 Aug 18;132(7):567-77. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.015218. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Circulation. 2015. PMID: 26187182 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of serum and glucocorticoid regulated kinase-1 as novel therapy for cardiac arrhythmia disorders.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 23;7(1):346. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00413-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28336914 Free PMC article.
-
Adverse cardiac remodeling: phosphoinositide 3-kinase, another unique factor in a multifactorial condition.Circulation. 2012 Oct 30;126(18):2175-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.138313. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Circulation. 2012. PMID: 23019295 No abstract available.
-
Serum and Glucocorticoid Regulated Kinase 1 in Sodium Homeostasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 10;17(8):1307. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081307. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27517916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1 (SGK1) as an emerging therapeutic target for cardiac diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2024 Oct;208:107369. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107369. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Pharmacol Res. 2024. PMID: 39209082 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 and the response to cell stress.Cell Stress. 2018 Dec 2;3(1):1-8. doi: 10.15698/cst2019.01.170. Cell Stress. 2018. PMID: 31225494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proanthocyanidins Maintain Cardiac Ionic Homeostasis in Aldosterone-Induced Hypertension and Heart Failure.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 4;22(17):9602. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179602. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502509 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-induced physiological hypertrophy initiates activation of cardiac progenitor cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jan 15;7(2):663-9. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 24551287 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-microbial peptide LL-37/CRAMP levels are associated with acute heart failure and can attenuate cardiac dysfunction in multiple preclinical models of heart failure.Theranostics. 2020 May 15;10(14):6167-6181. doi: 10.7150/thno.46225. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32483446 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpressed SIRT6 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and potentiates the therapeutic efficacy through metabolic remodeling.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023 Jun;13(6):2680-2700. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.03.019. Epub 2023 Mar 25. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023. PMID: 37425037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Undrovinas AI, Maltsev VA, Kyle JW, Silverman N, Sabbah HN. Gating of the late na+ channel in normal and failing human myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2002;34:1477–1489. - PubMed
-
- Cesario DA, Brar R, Shivkumar K. Alterations in ion channel physiology in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2006;35:601–610. ix–x. - PubMed
-
- Matsui T, Li L, MonteF d, Fukui Y, Franke TF, Hajjar RJ, Rosenzweig A. Adenoviral gene ransfer of activated phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and akt inhibits apoptosis of hypoxic cardiomyocytes in vitro. Circulation. 1999;100:2373–2379. - PubMed
-
- Matsui T, Tao J, del Monte F, Lee K-H, Li L, Picard M, Force TL, Franke TF, Hajjar RJ, Rosenzweig A. Akt activation preserves cardiac function and prevents injury after transient cardiac ischemia in vivo. Circulation. 2001;104:330–335. - PubMed
-
- Aoyama T, Matsui T, Novikov M, Park J, Hemmings B, Rosenzweig A. Serum and glucocorticoid-responsive kinase-1 regulates cardiomyocyte survival and hypertrophic response. Circulation. 2005;111:1652–1659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 HL089319/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL104156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KO8HL089319/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL050411/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL094677/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL050411/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL104370/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA027021/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL094677/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21HL104370/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM056203/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

